TitanMig 200D Operators Manual
Issue. A 1216
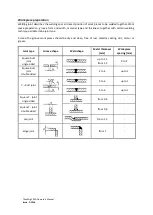
Due to these mixtures having a relatively low heat input, fusion defects and porosity can occur when
welding heavy sections due to the penetration profile, low fluidity and the rapid freezing of the weld
pool.
Carbon Steel – Intermediate content CO2 mixtures
Intermediate content CO2 mixtures (8-15% CO2) produce a higher heat input giving improved
characteristics and broader penetration profile.
These mixtures are more versatile than the low content CO2 mixtures and sound welds can be
produced over a wide range of material thickness.
These mixtures usually produce the most stable welding arc characteristics and are normally the best
general purpose shielding gases for Mild, Carbon and Low Alloy Steels.
High content CO2 mixtures
High content CO2 mixtures (16-23% CO2) allow for further improvements in the fusion characteristics
and the penetration profiles of the weld.
These mixtures are ideally suited for welding heavy sections especially in multi pass situations.
The stiff weld pools cool relatively slowly which aids welding and complete fusion to the weld side
walls.
Any entrapped gas has time to disperse before freezing of the weld pool occurs.
The arc is less stable than with the low content CO2 mixtures which may result in increased spatter
levels.
Welding current setting
Set the welding current after the above preparation. Short circuiting transfer is mainly fit for electrode
wires of diameter 0.6~1.2mm. As a guide for short circuit welding set the welding current according to the
table below.
Wire Diameter(mm)
Welding Current Range(A)
Optimal Current(A)
0.8
50-120
70-100
1.0
70-180
80-120
1.2
80-350
100-200
Welding speed selecting
The welding quality and productivity should be taken into consideration for the selecting of welding speed.
In the case that the welding speed increases, it weakens the protection effect and quickens the cooling. As
a consequence, it is not good for weld bead shaping. In the event that the speed is too slow, the work
piece will be burned through, and a good weld bead will be unavailable. In practical operation, the welding
speed should not exceed 50cm/min.
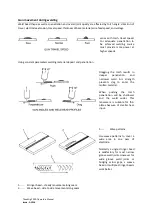
Wire Stick-out
The increase of the stick-out can improve the productivity, but too long stick-out may lead to excessive
spatter, wire breaking and unstable welding. Generally, the stick-out should be 10 times as the welding
wire diameter.
Shielding Gas flow selection
The protection effect is the primary consideration. Besides, the protection effect of inner-angle welding is
better than that of external-angel welding, so the gas flow in inner-angle welding should be lower. Less or
no shield gas is needed in FCAW. Refer to the table below for the recommended gas flow rates.
Welding Mode
Welding with thin wire
Welding with thick wire
Welding with thick wire
under high current
Gas Flow(L/m)
5~15
15~20
20~2