65
Rev Version 1.4.1
Rev Version 1.4.1
11. Click Save Changes and Reset.
The module restarts with the new settings.
Client 1 Configuration
1. Perform the same configuration steps as the access point configuration with the following differences:
•
Ensure that the Radio, System Address (ESSID) and Encryption key are the same as the access point.
•
Set the Operating Mode to
“Client.”
•
Change the IP addresses to 192.168.0.101.
2. When complete, set the DIP switch back to RUN and click Save Changes and Reset.
Client 2 Configuration
1. As for Client 1 above, but set the IP address as 192.168.0.102.
2. When complete, set the DIP switch back to RUN and click Save Changes and Reset.
Connecting Two Networks Together
This example describes how to configure a routed network.
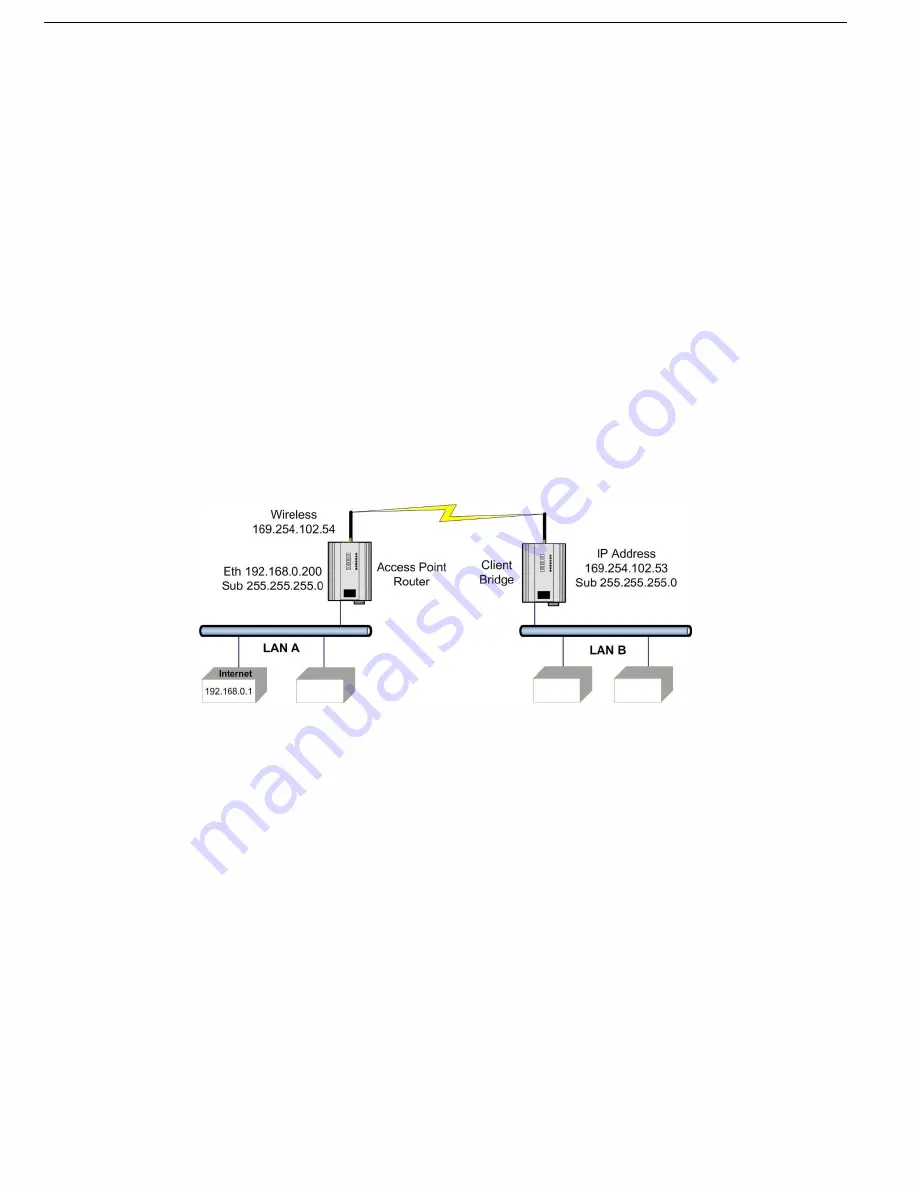
Figure 72 Example of Routed Network
LAN A Configuration
In this example, network A is connected to the Internet via a router at IP address 192.168.0.1. Devices on LAN A
that require a connection to devices on LAN B, should set their gateway IP addresses to the Ethernet address of
the WI-MOD-xxx-E-5W access point/router (192.168.0.200).
Devices on LAN A, that interact with devices on the Internet and LAN B should set their gateway IP address to
the Internet router (192.168.0.1), and then apply a routing rule for devices on Network B. On Windows-based PCs,
this may be achieved using the MS-DOS command ROUTE. For this example, the command would be: ROUTE
ADD 169.254.102.0 MASK 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.200. For more information on the DOS ROUTE command, see
section
“5.13 Utilities” on page 85.
LAN B Configuration
All devices on LAN B should be configured so that their gateway IP addresses are configured with the IP address of
169.254.102.54, which is the WI-MOD-xxx-E-5W access point/router.






























