VTSSD4
V. 01
–
15/05/2014
5
©Velleman nv
Leaded solder
Lead-free solder
Melting point
215 °C (419 °F)
220 °C (428 °F)
Normal operation
270
–
320 °C (518
–
608 °F)
300
–
360 °C (572
–
680 °F)
Production line operation
320
–
380 °C (608
–
716 °F)
360
–
410 °C (680
–
770 °F)
A good joint is assured if the iron's operating temperature is set within the parameters suitable for the type of
solder being used. The solder will flow too slowly if the temperature is too low; if the temperature is too high,
the flux in the solder may burn which will give rise to billowing white smoke. In turn, this will result in a dry
joint or in permanent damage to the PCB.
Important note:
Do not use temperatures higher than 410 °C (770 °F) for normal soldering or desoldering
purposes. You can use the device at higher temperatures for short periods, but this will shorten the lifespan of
the tip.
Desoldering
Recommended tip temperatures for desoldering are detailed below. They can vary from joint to joint.
For a small joint
320
–
360 °C (608
–
680 °F)
For a larger joint
370
–
400 °C (698
–
752 °F)
If the temperature is too low, the solder will flow too slowly, which may cause clogging in the desoldering tip. If
the temperature is too high, you may burn the PCB.
6.
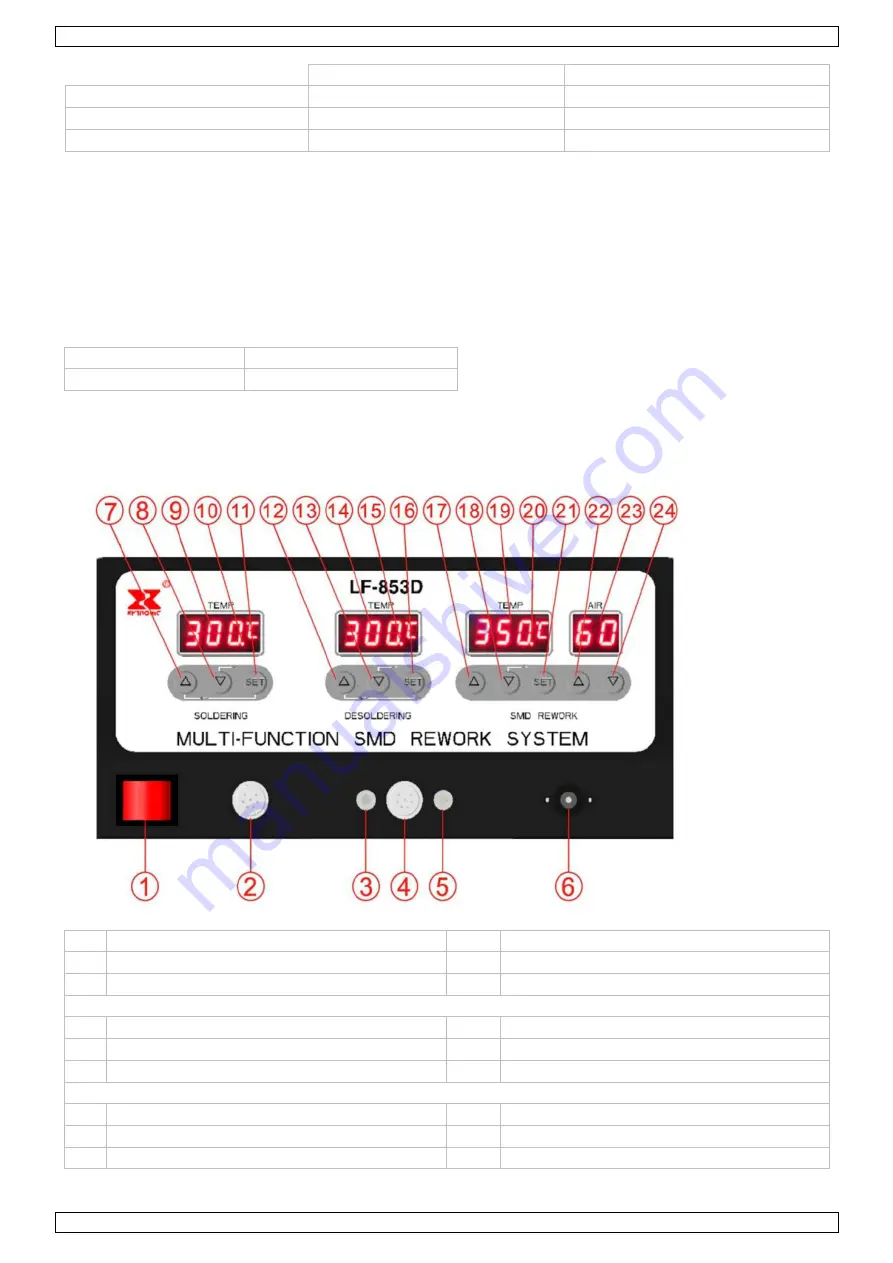
Overview
1
power switch
4
desoldering iron connection
2
soldering iron connection
5
desoldering vacuum connection
3
desoldering hot air connection
6
hot air connection
soldering function
7
UP button (
▲
) to increase temperature
10
heating indication
8
DOWN button (
▼
) to decrease temperature
11
SET button
9
temperature display
desoldering function
12
UP button (
▲
) to increase temperature
15
heating indication
13
DOWN button (
▼
) to decrease temperature
16
SET button
14
temperature display