TIG WELDING GUIDE
TIG Welding is a fusion procedure that uses an electric ARC created between
an infusible tungsten electrode and base material to be welded. For TIG
welding an inert gas must be used (Argon) which protects the welding bead.
If filling material is used, it is made up of rods suitable to the material to be
welded (steel, stainless steel, copper etc).
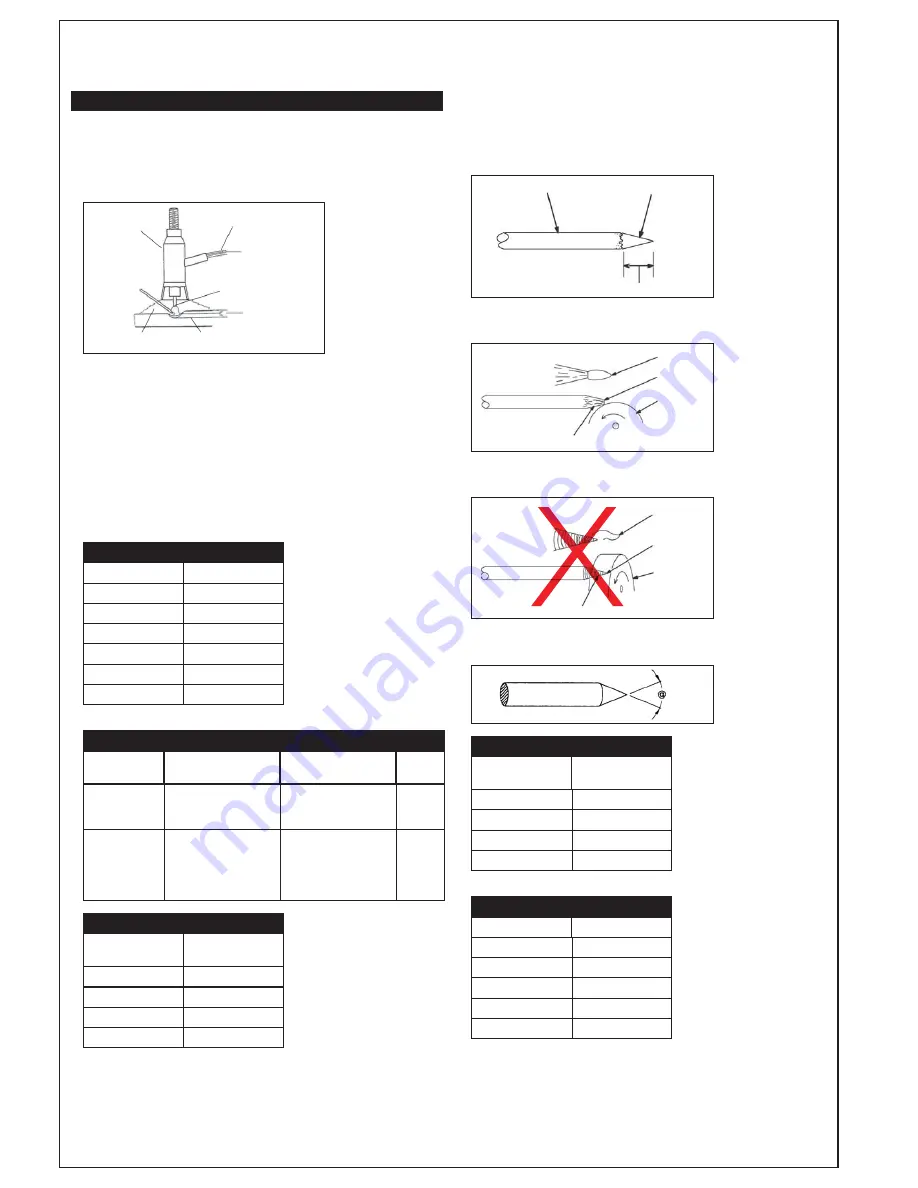
TIG Welding (Fig 15)
Torch
Rod
Protective Gas
Base Material
Penetration
Melted Area
Deposit
Tungsten Electrode
Inert Gas
Electric Current
In TIG mode, welding is possible in all positions: flat, angle, on the edge,
vertical and overhead. Furthermore, with respect to other types of welding, the
welding joint has greater mechanical resistance, greater corrosion resistance
and limited heating in the welded area which limits distortion. Welding can be
done even without weld material, guaranteeing a smooth, shiny weld with no
impurities or slag.
TIG ELECTRODE SELECTION AND PREPARATION
Electrode Polarity
Connect the TIG torch to the negative (-) torch terminal and the work lead to
the positive (+) work terminal for direct current straight polarity. Direct current
straight polarity is the most widely used polarity for DC TIG welding. It allows
limited wear of the electrode since 70% of the heat is concentrated at the work
piece.
Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Electrode Diameter
DC Current (Amps)
1.0mm (0.040”)
30 - 60
1.6mm (1/16”)
60 - 115
2.4mm (3/32”)
100 - 165
3.2mm (1/8”)
135 - 200
4.0mm (5/32”)
190 - 280
4.8mm (3/16”)
250 - 340
Tungsten Electrode Types
Electrode Type
(Ground Finish)
Application
Features
Colour
Code
Thoriated 2%
DC welding of mild
steel, stainless steel
and copper.
Excellent arc atarting;
long life; high current
capacity.
Red
Ceriated 2%
DC welding of mild
steel, stainless steel
and copper.
Longer life; more stable
arc; easier starting;
wider current range;
narrower, more con-
centrated arc.
Grey
Guide For Selecting Filler Wire Diameter
Filler Electrode
Diameter
DC Current (Amps)
1.6mm (1/16”)
20 - 90
2.4mm (3/32”)
65 - 115
3.2mm (1/8”)
100 - 165
4.8mm (3/16”)
200 - 350
PREPARING TUNGSTEN FOR DC ELECTRODE NEGATIVE (DCEN) WELDING
2.5 x Electrode Diameter (Fig 16-1)
Grind end of tungsten on fine grit, hard abrasive wheel before welding. Do not
use wheel for other jobs or tungsten can become contaminated causing lower
weld quality.
Tungsten Electrode
Tapered End
2.5 x Electrode Diameter
Ideal Tungsten Preparation - Stable ARC (Fig 16-2)
Diameter of the flat determines amperage capacity.
Stable ARC
Flat
Grinding
Wheel
Straight Ground
Wrong Tungsten Preparation - Wandering ARC (Fig 16-3)
Diameter of the flat determines amperage capacity.
ARC Welder
Point
Grinding
Wheel
Radial Ground
x
Pointing the Electrode (Fig 17)
The electrode should be pointed according to the welding current.
Electrode Angles
Angle @
Range of Current
(Amps)
30
O
0 - 30
60-90
O
30 - 120
90-120
O
120 - 250
120
O
> 250
Shielding Gas Selection
Aloy
Shielding Gas
Carbon Steel
Welding Argon
Stainless Steel
Welding Argon
Nickel Alloy
Welding Argon
Copper
Welding Argon
Titanium
Welding Argon
ZZZVWUDWDFRQ]




































