Construction
0---15
20--- 8
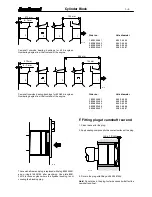
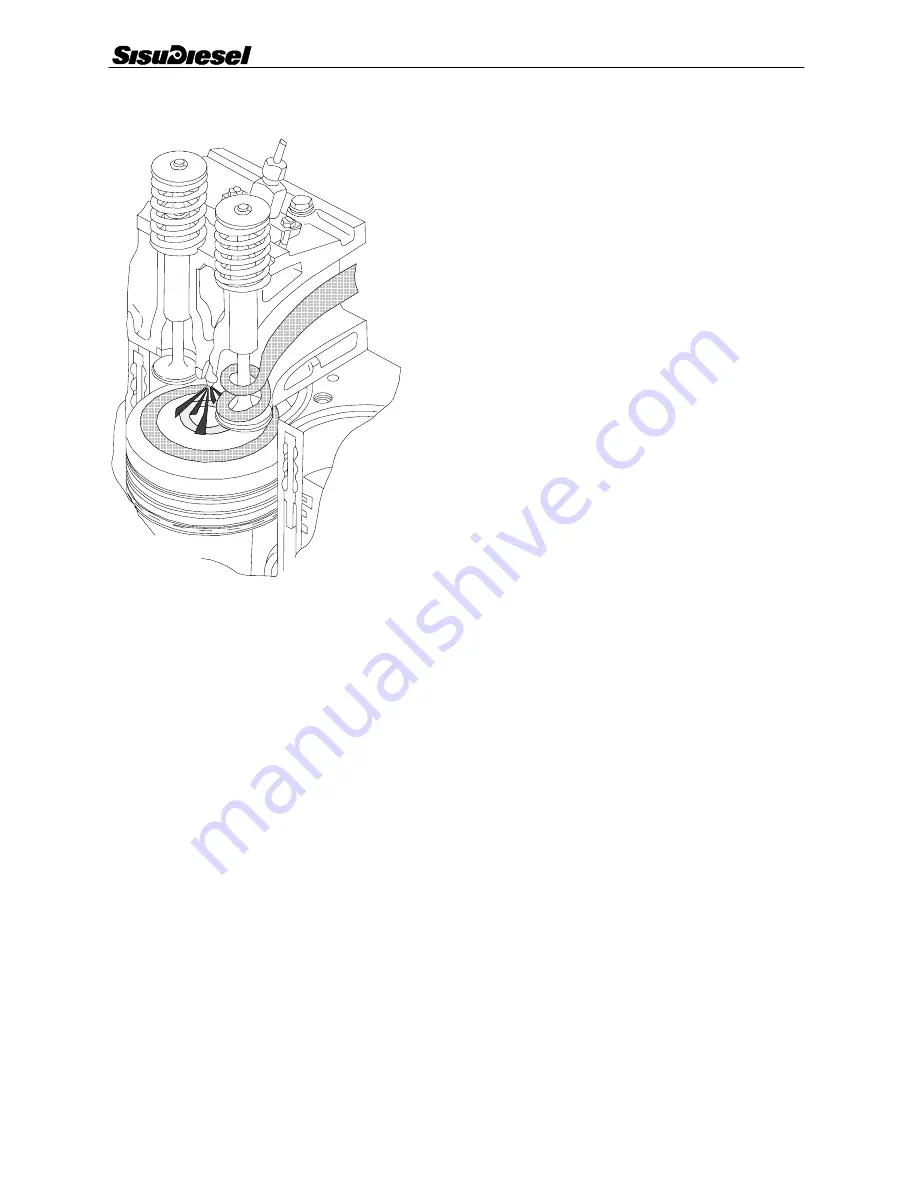
Cylinder head
320--- and 420---engines have one cylinder head.
620/634---engines have two cylinder heads which are ex-
changeable with each other and also with the cylinder head
on the 320---engine. Each cylinder has its own inlet and ex-
haust ports located on either side of the head. Between hotex-
haust valves a cool inlet valve is fitted to balance the thermal
load.
Cylinder head bolts are high tensile bolts which are tightened
up to yield limit using angle tightening principle. Due to the
large stretch the tightening forces are keptconstant during the
whole lifetime and retightening is unnecessary.
The injector locations are machined directly into the cylinder
head. The inlet and exhaust valve guides are identical and can
be interchanged. In addition, the exhaust valves are equipped
with replaceable valve seat inserts.
Valve mechanism
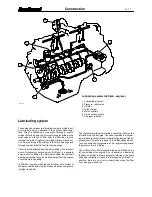
The valve mechanism is operated by the camshaft which is lo-
cated in the cylinder block. The drive is transferred with the
help of tappets and pushrods. The camshaft gear wheel is
fitted with a press fit and fixed with a key. Each bearing is lubri-
cated by the force feed lubrication system through drilled oil-
ways in the motor block.
Crank mechanism
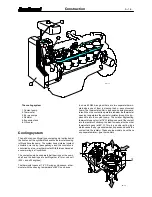
The crankshaft is forged from chrome alloy special steel and
is induction hardened at the bearing and sealing surfaces.
This makes it possible to grind bearings four times without a
new heat treatment. Gear wheels are located at the front end
of the crankshaft. They are a press fit, and drive the idler wheel
and oil pump. In addition, the front end of the crankshaft has
splines for the hub of the V---belt pulley. An oil deflector ring
is fitted between the hub and gear wheel, and a dust shield is
fitted on the hub in order to protect the seal.
The crankshaft is supported on the cylinder block by main
bearings which are placed on both sides of each cylinder.
Thus there is one main bearing more than cylinders. The
crankshaft thrust washers are placed in both sides of the rear-
most main bearing.
At the rear end of the crankshaft there is fitted a flywheel on
which is a press---fit a starter ring gear. The forged connecting
rod has an I---section cross---section. The bearing location at
the bottom end of the connecting rod is split, and the bearing
cup is secured by two special bolts and nuts. The upper part
has a wedge---shaped bearing location, in which the piston
pin bearing bushing is fitted with a press fit.
The piston is made of an eutectic aluminium alloy. In the
upper face of the piston there is a combustion chamber. The
shape of the chamber is intended to maximise the mixture of
air and fuel. The piston has three rings. The upper molyb-
denum---coated ring has a wedge---shaped cross---section.
On natural aspirated engines and on slight supercharged en-
gines the upper ring is right---angled. The middle ring is tap-
ered and it fits into its groove. The taper taking up the clear-
ance. The oil control ring is spring loaded and it has a
two---stage, chromed scraping edge.
On the turbocharged engines the upper ring location is
formed in a cast iron ring which is cast in the piston. In addi-
tion, the piston on supercharged engines is graphite coated
to ensure correct running---in.
Four---cylinder engines (420) are equipped with a balancer
unit. The eccentric weights, which rotate at twice the engine
speed, even out the vibration forces exerted by the movement
of the pistons and the crank mechanism.