Chapter 7-12
CE33 Echosounder operation
7.10 How the echosounder works
When the CE33 is turned on, the processor begins to
send electrical pulses to the transducer. The ceramic
resonators in the transducer has a special property
which enables it to change dimensions slightly when
a varying voltage is applied.
The voltage is thus converted to mechanical vibra-
tions (sound waves) which are then transmitted down
through the water.
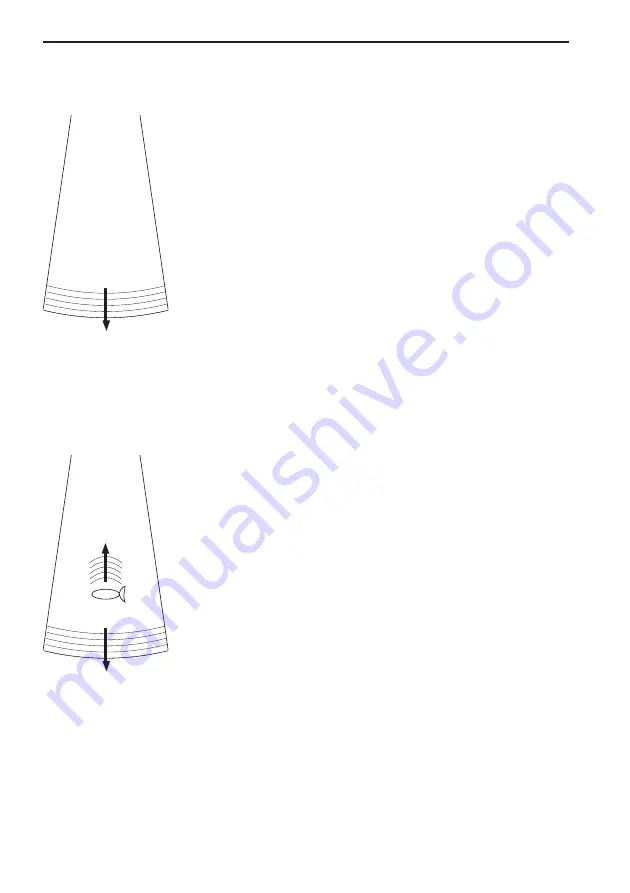
See Fig. 1.
Fig. 1 Transmi ed ‘ping’
from the transmi er/receiver.
The sound waves move through the water until they
encounter a change in density, such as a fish or the
bottom. This causes the sound waves to ‘echo’ back
up through the water. When the reflected sound
waves (echoes) hit the transducer, the ceramic disk
vibrates at the same frequency. This generates a
varying voltage between the disk surfaces. This volt-
age goes back up through the cable to the receiver.
The CE33 processes the signals and presents them on
the display screen.
See Fig. 2.
Fig. 2 The up arrow indicates:
Echo returning to the receiver.
The down arrow indicates:
Transmi ed pulse.
Summary of Contents for CE33 ChartSounder
Page 14: ...Chapter 1 8 CE33 Introduction and safety summary...
Page 44: ...Chapter 3 22 CE33 Chart menu and INFO windows...
Page 60: ...Chapter 4 16 CE33 Position menu...
Page 76: ...Chapter 5 16 CE33 Waypoint route menu...
Page 126: ...Chapter 9 12 CE33 Setup menu Page 1 of 2 Page 2 of 2...
Page 130: ...Chapter 10 2 CE33 Installation and service Other important settings continued...
Page 162: ...Appendix C 8 CE33 C MAP attributes...
















































