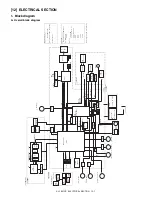
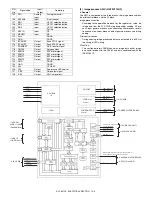
AL-1651CS ELECTRICAL SECTION 12 - 8
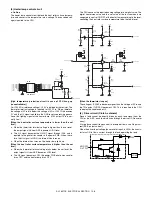
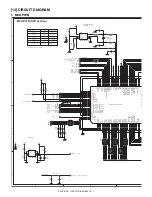
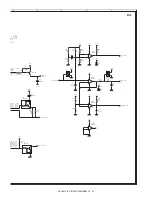
(5) Heater lamp control circuit
a. Outline
The heater lamp control circuit detects the heat roller surface tempera-
ture, and converts the temperature into a voltage. The converted volt-
age is inputted to the CPU.
The CPU converts the inputted analog voltage into a digital value. The
digital conversion value and the set value of the test command are
compared to control ON/OFF of the heater lamp according to the level,
controlling the heat roller surface temperature to be the fixed level.
[High temperature protection circuit in case of CPU hung up
(uncontrollable)]
For IC22 3Pin (reference voltage), +3.3V is divided by the resistor. The
thermistor terminal voltage is inputted to IC22 2Pin. When, therefore,
the voltage at 2Pin falls below the voltage at 3Pin, IC22 1Pin becomes
"H" and the HL signal is pulled to the GND level, suppressing genera-
tion of the lighting signal of the heater lamp. (IC22 output 1Pin is nor-
mally Low.)
[When the heat roller surface temperature is lower than the set
level]
a. When the thermistor terminal voltage is higher than the set level,
the output signal HL from ASIC becomes HIGH level.
b. This HL signal becomes the HLOUT signal through IC26, and is
inputted to the photo triac coupler in the power PWB. When, there-
fore, the HL signal is HIGH, the internal triac turns on.
c. When the internal triac turns on, the heater lamp lights up.
[When the heat roller surface temperature is higher than the set
level]
a. When the thermistor terminal voltage falls below the set level, the
output signal HL from ASIC becomes LOW level.
b. The HL signal becomes LOW, the power PWB photo triac coupler
turns OFF, and the heater lamp turns OFF.
[When the thermistor is open]
The voltage at IC22 6Pin becomes higher than the voltage at 5Pin, and
the 7Pin output THOPEN becomes LOW. This is inputted to the CPU
to display the trouble code H2.
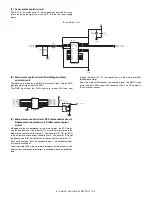
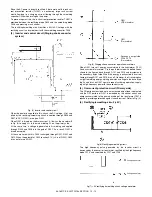
(6) Driver circuit (Clutch, solenoid)
Since a load cannot be directly driven by each load signal from the
CPU or the ASIC, each load is driven through the driver IC (transistor
array).
A large drive current (load current) is ordained from a small input cur-
rent (ASIC output current).
When the driver input voltage (base resistor input) is HIGH, the transis-
tor turns ON to flow a current through the load, operating the load.
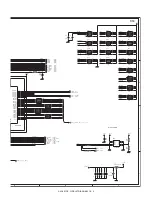
R68
7.5kF
21
R71
4.3kF
21
D1
MA700
1
2
R67
1MF
21
R66
1kF
21
R70
10kF
21
R69
1kJ
21
C111
22000p
1
2
C113
0.1u
1
2
R81
300J
2
1
R82
100J
2
1
C112
0.1u
1
2
R83
1.2kF
21
R85
10kF
21
R84
10kJ
21
C114
22000p
1
2
D4
1SS355
1
2
R86
240J
21
R87
240J
21
IC22A
KIA393F
3
2
1
8
4
+
-
C110
0.1u
1
2
IC22B
KIA393F
5
6
7
8
4
+
-
IC24A
KIA358F
3
2
1
8
4
+
-
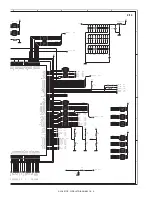
IC26
KID65503F
1B
1
2B
2
3B
3
4B
4
5B
5
6B
6
7B
7
G
8
NC
9
1C
16
2C
15
3C
14
4C
13
5C
12
6C
11
7C
10
Q2
KRA119S
1
2
3
D2
KDS226
2
1
3
D3
KDS226
2
1
3
INT5V
12V
VCC3
VCC3
VCC3
12V
VCC3
12V
12V
12V
VCC3
5V
MRPS1
HL
LDEN
PMCLK
FTH
HLOUT
PMCLK_A
MRPS_1
/LDEN
MRPS_2
FTH
RTH
THOPEN
RTH_IN
MRPS2
MRPS3
MRPS_3
(11-B2)
(11-B2)
(6-A1)
(6-A1)
(6-A1)
(5-E3)
(2-D1)
(2-C1)
(2-D1)
(2-D1)
(2-C1)
(1-A2)
(10-B3)
(1-A3)
(4-A4)
(5-B2)
(11-C1)
LOAD
+24V
ASIC/CPU
OUT PUT
LOAD