MultiMediaCard Product Manual
SanDisk MultiMediaCard Product Manual Rev. 2 © 2000 SANDISK CORPORATION
63
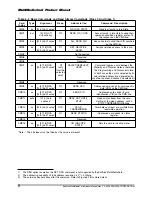
6.1.4
Data Write
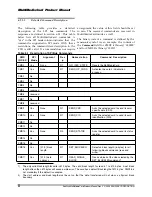
As for the read operation, while in SPI mode the MultiMediaCard supports single block write only.
Upon reception of a valid write command (MultiMediaCard CMD24) the card will respond with a
response token and will wait for a data block to be sent from the host. CRC suffix and start address
restrictions are identical to the read operation (refer to Figure 6-3). The only valid block length,
however, is 512 bytes. Setting a smaller block length will cause a write error on the next write
command.
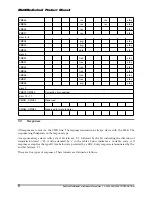
From
Host to
Card
From
Card to
Host
Data From
Host to Card
New Command
From Host
DataIn
DataOut
Command
Response
Command
Data Block
Data_Response Busy
Data
Response
and Busy
From Card
Figure 6-3 Write Operation
After a data block is received the card will
respond with a data-response token and if the
data block is received with no errors it will be
programmed. As long as the card is busy
programming, a continuous stream of busy tokens
will be sent to the host (effectively holding the
dataOut line low).
Once the programming operation is completed, the
host must check the results of the programming
using the SEND_STATUS command (CMD13).
Some errors (e.g. address out of range, write
protect violation, etc.) are detected during
programming only. The only validation check
performed on the data block and communicated to
the host via the data-response token is CRC.
Resetting the CS signal while the card is busy,
will not terminate the programming process. The
card will release the dataOut line (tristate) and
continue to program. If the card is reselected
before the programming is done, the dataOut line
will be forced back to low and all commands will
be rejected.
Resetting a card (using CMD0) will terminate any
pending or active programming operation. This
may destroy the data formats on the card. It is the
host’s responsibility to prevent it.
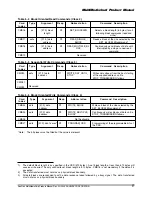
6.1.5
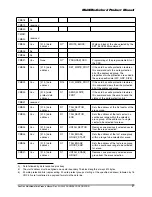
Erase & Write Protect Management
The erase and write protect management
procedures in the SPI mode are identical to the
MultiMediaCard mode. While the card is erasing
or changing the write protection bits of the
predefined sector list it will be in a busy state and
will hold the dataOut line low. Figure 6-4
illustrates a “no data” bus transaction with and
without busy signaling.
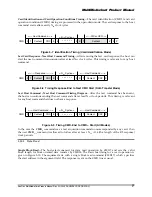
From
Host to
Card
From
Card to
Host
DataIn
DataOut
Command
Response
Command
Response
Busy
From
Host to
Card
From
Card to
Host
Figure 6-4 “No Data” Operations