MultiMediaCard Product Manual
SanDisk MultiMediaCard Product Manual Rev. 2 © 2000 SANDISK CORPORATION
59
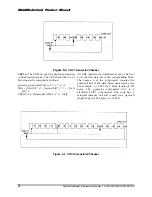
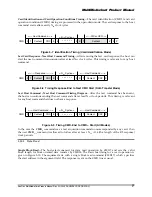
Figure 5-13 Timing Of The Block Write Command
If the MultiMediaCard does not have a free data receive buffer, the card indicates this condition by
pulling down the data line to LOW. The card stops pulling down the data line as soon as at least one
receive buffer for the defined data transfer block length becomes free. This signaling does not give any
information about the data write status which must be polled by the host.
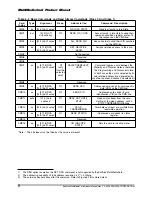
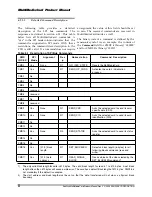
Multiple Block Write
—In multiple block write mode, the card expects continuous flow of data blocks
following the initial host write command. The data flow is terminated by a stop transmission command
(CMD12). Figure 5-14 describes the timing of the data blocks with and without card busy signal.
Figure 5-14 Timing of Multiple Block Write Command
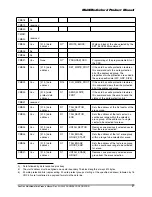
In write mode, the stop transmission command works similarly to the stop transmission command in the
read mode. Figures 5-15 to 5-18 describe the timing of the stop command in different card states.
Figure 5-15 Stop Transmission During Data Transfer from the Host
The card will treat a data block as successfully received and ready for programming only if the CRC
data of the block was validated and the CRC status token sent back to the host. Figure 5-16 is an
example of an interrupted (by a host stop command) attempt to transmit the CRC status block. The
sequence is identical to all other stop transmission examples. The end bit of the host command is
followed, on the data line, with one more data bit, end bit and two Z clock for switching the bus
direction. The received data block, in this case is considered incomplete and will not be programmed.
Figure 5-16 Stop Transmission During CRC Status Transfer from the Card