12 | SAMLEX AMErICA INC.
1.3.4 electro-Magnetic interference (eMi) and eMC Compliance
These inverters contain internal switching devices that generate conducted and radiated
electromagnetic interference (EMI). The EMI is unintentional and cannot be entirely eliminated.
The magnitude of EMI is, however, limited by circuit design to acceptable levels as per limits laid
down in the European EMC Directive 2014/30/EU for Class A limits. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated
in a
residential environment
. These inverters can conduct and radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. The effects of EMI will also depend upon a number of factors external
to the inverter like proximity of the inverter to the EMI receptors, types and quality of connecting
wires and cables etc. EMI due to factors external to the inverter may be reduced as follows:
•
Ensure that the inverter is firmly grounded to the Ground System of the building or the vehicle.
•
Locate the inverter as far away from the EMI receptors like radio, audio and video devices
as possible.
•
Keep the DC side wires between the battery and the inverter as short as possible.
•
Do NOT keep the battery wires far apart. Keep them taped together to reduce their
inductance and induced voltages. This reduces ripple in the battery wires and improves
performance and efficiency.
•
Shield the DC side wires with metal sheathing / copper foil / braiding.
•
Use coaxial shielded cable for all antenna inputs (instead of 300 ohm twin leads).
•
Use high quality shielded cables to attach audio and video devices to one another.
•
Limit operation of other high power loads when operating audio / video equipment.
1.3.5 Characteristics of Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are extensively used to convert the incoming AC power into
various voltages like 3.3V, 5V, 12V, 24V etc. that are used to power various devices and circuits
used in electronic equipment like battery chargers, computers, audio and video devices, radios
etc. These power supplies use large capacitors in their input section for filtration. When the
power supply is first turned on, there is a very large inrush current drawn by the power supply as
the input capacitors are charged (The capacitors act almost like a short circuit at the instant the
power is turned on). The inrush current at turn-on is several to tens of times larger than the rated
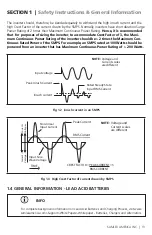
rMS input current and lasts for a few milliseconds. An example of the input voltage versus input
current waveforms is given in fig. 1.2. It will be seen that the initial input current pulse just after
turn-on is > 15 times larger than the steady state rMS current. The inrush dissipates in around 2
or 3 cycles i.e. in around 40 to 60 milliseconds for 50 Hz sine wave.
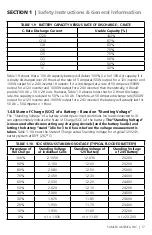
further, due to the presence of high value of input filter capacitors, the current drawn by an SMPS
(With no Power factor correction) is not sinusoidal but non-linear as shown in fig 1.3. The steady
state input current of SMPS is a train of non-linear pulses instead of a sinusoidal wave. These
pulses are two to four milliseconds duration each with a very high Crest factor of around 3. Crest
factor is defined by the following equation:
CreSt FACtor = PeAk VALue ÷ rMS VALue
Many SMPS units incorporate “Inrush Current Limiting”. The most common method is the NTC
(Negative Temperature Coefficient) resistor. The NTC resistor has a high resistance when cold
and a low resistance when hot. The NTC resistor is placed in series with the input to the power
supply. The higher cold resistance limits the input current as the input capacitors charge up. The
input current heats up the NTC and the resistance drops during normal operation. However,
if the power supply is quickly turned Off and back ON, the NTC resistor will be hot so its low
resistance state will not prevent an inrush current event.
SECTIOn 1 |
Safety Instructions & general Information