24
Rockwell Automation Publication 442G-UM002A-EN-P - December 2016
Chapter 3
Use the Multifunctional Access Box in an Integrated Safety Controller-based System
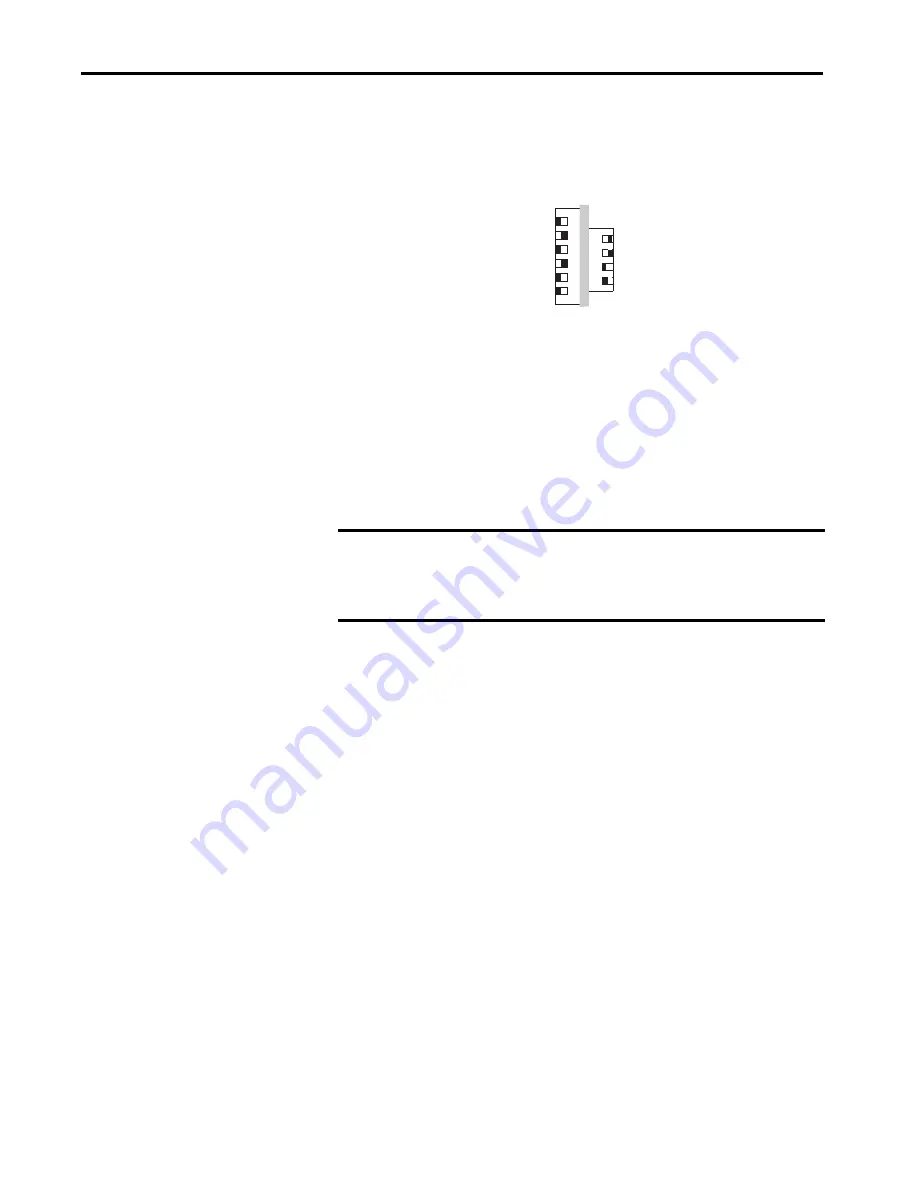
Figure 16 - Example Network Address DIP Switches
This example shows the switches set at 10100011 (163) with a network
address of 192.168.1.163.
Set the IP Address with a
BOOTP/DHCP Server
The BOOTP/DHCP server is a standalone server that you can access from
either of these locations:
• Programs > Rockwell Software > BOOTP-DHCP Server
If you have not installed the server, you can download and install it from
http://www.ab.com/networks/ethernet/bootp.html.
• Tools directory on the Studio 5000™ installation CD
The BOOTP/DHCP server also limits the possibility of assigning duplicate
IP addresses.
If you use the BOOTP/DHCP server in an uplinked subnet where an
enterprise DHCP server exists, a module can get an address from the enterprise
server before the Rockwell Automation utility sees the module. If necessary,
disconnect from the uplink to set the address and configure the module to
retain the static address before reconnecting to the uplink. This is not a
problem if you have configured the node names in the module and leave
DHCP enabled.
To set the IP address with a BOOTP/DHCP server, follow these steps.
1. Start the BOOTP/DHCP software.
2. From the Tools menu, choose Network Settings.
3. If appropriate for the network, type the Subnet Mask, Gateway address,
Primary and/or Secondary DNS address, and Domain Name.
3
6
1
2
5
1
2
34
4
n.c.
DHCP
IP-Bit 7
IP-Bit 6
IP-Bit 5
IP-Bit 4
IP-Bit 3
IP-Bit 2
IP-Bit 1
IP-Bit 0
OFF ON
ON OFF
IMPORTANT
Before you start the BOOTP/DHCP server, make sure that you have the
ethernet address (MAC ID) of the module. The MAC ID is on a label on the
side of the module and uses an address in a format similar to the following:
00-0b-db-14-55-35






























