EN-10
Digital Optical:
Digital optical utilizes one cable to pass digital audio information (no video). A digital optical
cable offers a high-quality digital connection and passes multi-channel encoded audio between a source
component and an audio output device.
Digital Coaxial:
Digital coaxial utilizes one cable to pass digital audio information (no video). A digital coaxial
cable offers a high-quality digital connection and passes multi-channel encoded audio between a source
component and an audio output device.
NOTE!
The ‘RCA’ style end of a digital coaxial cable is identical to those found on common left/right analog
RCA cables. However, a cable designed specifically for digital coaxial connections should be employed—do
not use a standard left/right analog RCA style cable because it may not be up to the task of handling the high
bit-rate necessary for a reliable digital connection.
Left/Right Analog RCA:
Left/right analog RCA cables are used to pass audio information (no video). An analog
RCA cable can only be used to pass a single channel of audio information between a source component and audio
output device. To achieve two-channels of audio (left/right) you will find that analog RCA cables come bundled as
a stereo pair (2 connectors on each end). Analog RCA connections are not capable of passing the digital encoding
required to reproduce multi-channel audio and thus should not be used with source components where you
desire surround sound output. Older gaming consoles, portable media player docks, VCRs and similar source
components (which are not capable of playing multi-channel encoded content) will often offer connection only
through left/right analog RCA cables. Additionally, users may find source components such as digital media player
docks that utilize a special cable with a 3.5mm ‘headphone style’ jack on one end, and two analog RCA connectors
on the opposite end.
AN INTRODUCTION TO AUDIO CABLES
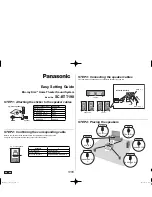
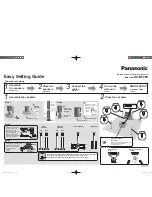
ROUTING SOURCES VIA A DIGITAL (Optical or
Coaxial) CONNECTION, WITH THE TELEVISION
USED TO SWITCH BETWEEN INPUTS
Some users will choose to route all sources (ex. DVD player, cable
box, game console, media streamer, etc.) to their television via
a digital (optical or coaxial) connection and use the television
to switch between audio/video sources. The advantage of this
connection method is that only one audio cable (either a digital
optical or digital coaxial cable) needs to connect between
the television and the Soundscape. Changing the input on
your television will change the audio signal being sent to the
Soundscape (without having to change the input setting.
A few important points to remember when connecting your
Soundscape:
•
Digital optical and digital coaxial connections will provide the
highest audio fidelity when connecting to the Soundscape.
•
Your Soundscape has an advanced, built-in digital
decoder. However, if your Soundscape is not producing
sound or surround sound from your Blu-ray player, DVD
player, or other multi-channel audio-capable source
through your TV, you may need to set the player’s digital
audio output to “Bitstream” (also called “Raw”, “Direct
Digital”, or “High Bit Rate”). If “PCM” is selected you’ll lose
the multi-channel encoded sound. Some players only
require you to turn PCM off to configure for multi-channel
encoded sound. Please refer to your player’s owners
manual for more detailed information.
•
Audio-only sources capable of only stereo output (such
as a portable media player docks or CD player) will often
connect directly to the Soundscape via the left/right
analog RCA inputs.