MW1008P, user manual
13
Capacitors :
Capacitors are measured in Farads. The basic construction of a capacitor is a dielectric material
between two electrodes. The many different types of capacitors available are classed according to
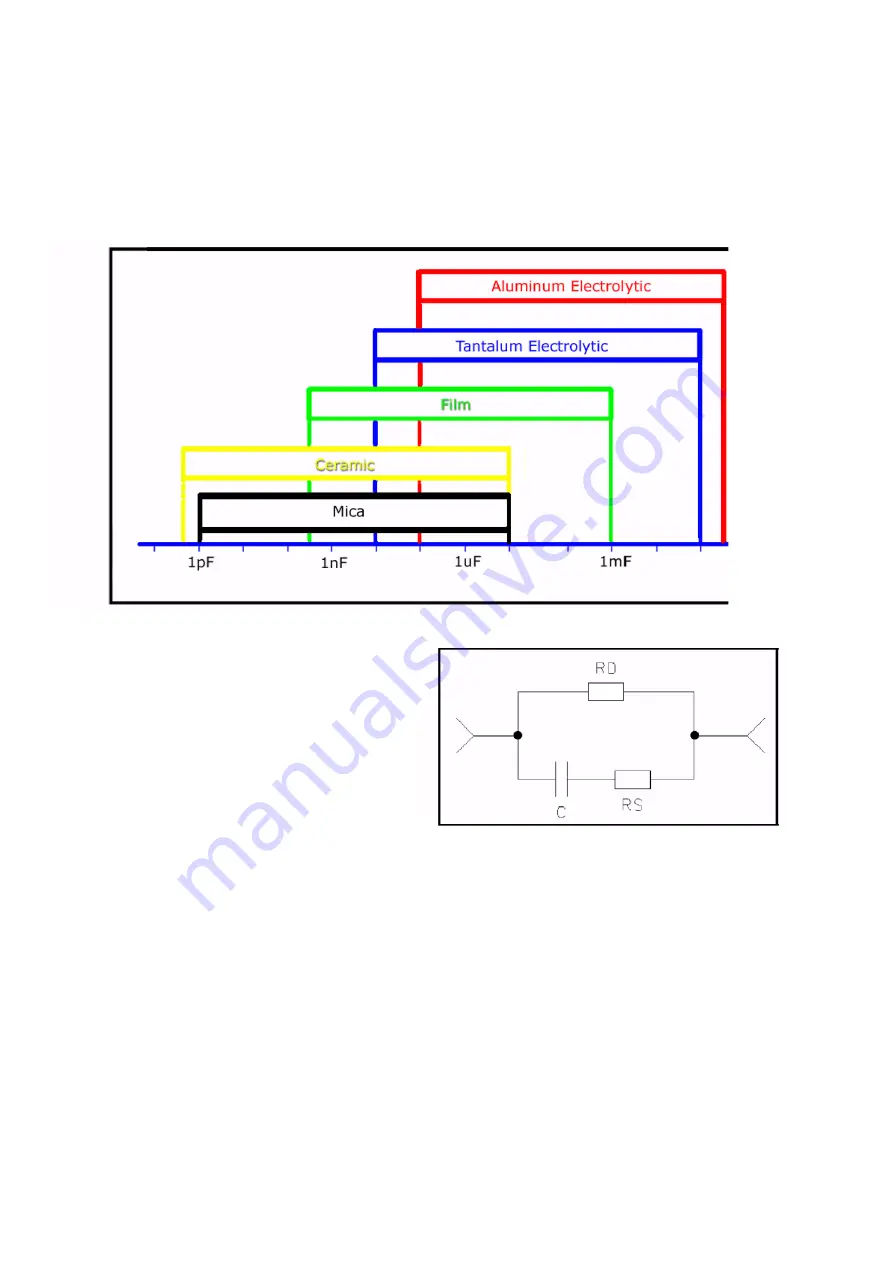
their dielectric types. The figure below shows the range of generic capacitance values for standard
types.
A capacitor can be modeled as a pure
capacitor C with some parasitic elements,
see the figure below. RS is the actual series
resistance, comprised of the lead resistance
and the foil resistance. RS is generally very
low (a few mil). RD symbolizes the
dielectric loss. Its value changes with
frequency.
Dissipation factor, also known as loss
tangent, is the ratio of the series
resistance to the reactance. It indicates the capacitor quality. A low D indicates a nearly pure
capacitor. In order to achieve reliable measurement a short zero must be performed before any
ESR or D measurement because in this case the series resistor can be very small. Like most
everything else about capacitors, it changes with time, frequency, and temperature. ESR is a
single resistive value of a capacitor representing all real losses. It includes effects of the
capacitor's dielectric loss.
Electrolytic Capacitors:
The accurate measurement of electrolytic capacitors, particularly large value caps, can present
unique requirements. The MW1008 LCR meter applies an AC signal to the DUT. To test some
polarized components, such as electrolytic and tantalum capacitors, it may be preferable to use
only positive voltages. During normal operation, the AC current source swings negative 50%
of the time, which results in an inverse polarization of the capacitor under test. To prevent this
inverse polarization, a DC bias can be applied to prevent the voltage across the part from














































