5
1
Ov
er
vie
w of functions
1. Overview of functions
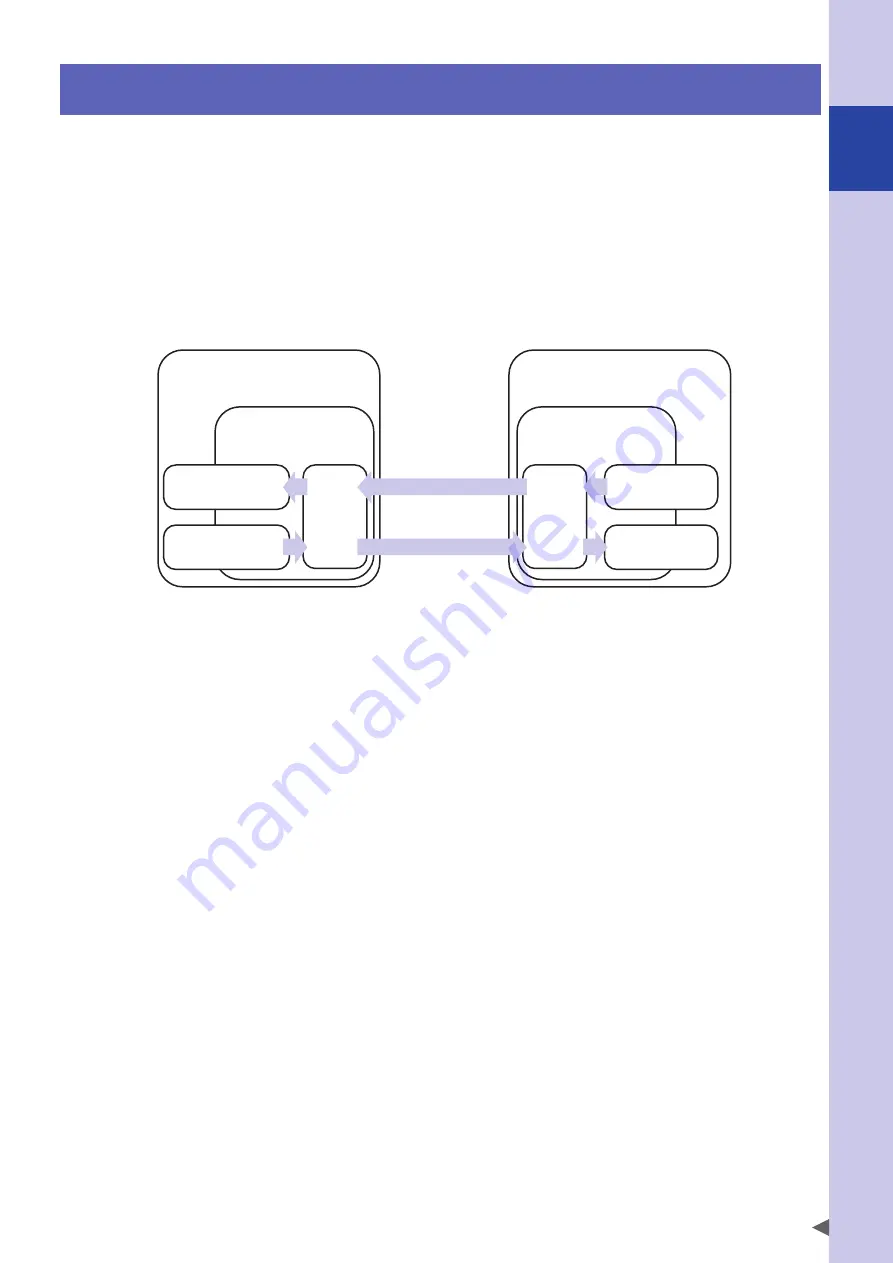
A network interface unit is a device that transmits and receives I/O information via a communication protocol
between a controller and a host control device.
We provide a lineup of products that support fieldbus (DeviceNet, PROFIBUS, etc.) or industrial Ethernet
(EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, etc.).
In any of these networks, the robot controller (slave device) operates in accordance with commands via I/O
control from a host (master device).
While acting as distributed I/O for the host control device, the network interface unit simultaneously shares
I/O information with the controller. The I/O update cycle time between the controller and the network
interface unit is 5 ms.
The I/O update cycle time between the network interface unit and the host control device will vary depending
on the structure of the applicable network.
←
Status output
Host control device
Network unit
(master / I/O controller)
Input
m, m+1, ..., m+x
Output
n, n+1, ..., n+y
Output
SO, SOW
Input
SI, SIW
Network unit
(slave / distributed I/O device)
Robot controller
(robot, I/O control)
←
General-purpose I/O
→
Conversion
Conversion
Command input
→
I/O consists of a general-purpose input/output area, and a dedicated input/output area that has specific
significance such command input and status output that is optimized for control of robot controllers. Using
these, the robot controller can be controlled from the host control device.
The following methods can be used for control via I/O. Combining these methods makes it possible to control
the robot.
1.
Controlling the robot controller directly using simple commands and status queries via remote
I/O's dedicated input/output.
Example) Dedicated input: cancel emergency stop, servo on, reset, start program execution, etc.
Dedicated output: CPU_OK, return-to-origin complete, etc.
2.
Using remote commands to programlessly control the robot controller directly with advanced
instructions and status queries.
Example) < Transmission >
SIW0 = 0x1031 (absolute reset command for robot no.1)
SIW2 = 0x0015 (axis designation: axis 1 through axis 4)
< Reception >
SOW = 0x0100 (executing command)
↓
SOW = 0x0200 (normal end)
3.
Using remote I/O's general-purpose input/output to exchange desired information with an
external peripheral device, and load it into a robot program or sequence program for execution.
Example) WAIT SI(20)=1, 1000 ; Wait until SI(20) turns on; stop command if it does not turn on after 1 second
OUT SO2(), 200
; SO(27--20) turns on, and turns off after 200 ms
* For details on remote I/O and remote commands, refer to the Remote I/O Manual. For details on robot programs, refer
to the YRCX Programming Manual.
Summary of Contents for SCARA Robots YRCX Series
Page 1: ... 7 6HULHV DW 1R 1 352 1 7 86 5 6 0 18 6 5 5RERWV 5 6HULHV ...
Page 2: ......
Page 41: ......
Page 43: ......
Page 44: ... DW 1R 1 XWKRUL HG LVWULEXWRU 3ULQWHG LQ XURSH ...










































