EN-24
Troubleshooting
Fault and Alarm Detection
Faults and Alarms are functions that indicate unusual inverter / application conditions.
An alarm does not necessarily switch of the inverter but a message is displayed on the keypad and an alarm
output is generated at the multi-function outputs (H2-01 to H2-03) if programmed. An alarm automatically
disappears if the alarm condition is not present anymore.
A fault switches the inverter off immediately, a message is displayed on the keypad and the fault output is
switched. The fault must be reset manually after the cause has been removed.
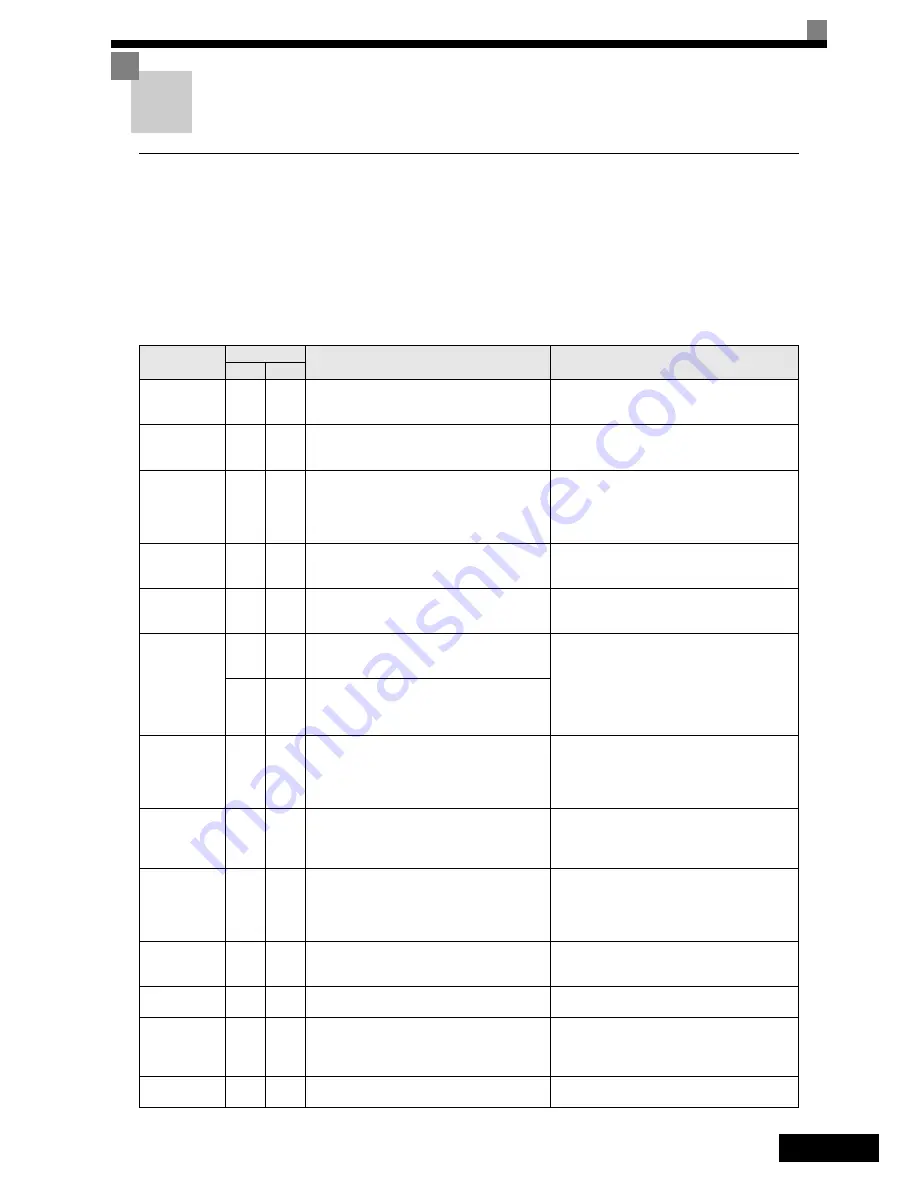
The following tables shows a list of faults and alarms with their corrective actions.
Display
Displayed as
Meaning
Corrective Actions
Alarm
Fault
BUS
Option Com Err
(flashing)
Option Communications Alarm
After initial communication was established, the con-
nection was lost.
Check the connections and all user-side software con-
figurations.
CF
Out of Control
A torque limit was reached continuously for 3 sec-
onds or longer during a deceleration stop in Open
Loop Vector control.
Check the motor parameters.
CPF00
CPF01
COM-
ERR(OP&INV)
• Digital Operator/LED Monitor Communication
Fault 1 / 2
• Communication fault between Operator and
inverter
• CPU External RAM Fault
• Disconnect the Digital Operator/LED Monitor and
then connect it again.
• Replace the Inverter.
• Cycle the Inverter power supply.
• Replace the Inverter.
CPF02 - CPF 04
• Baseblock circuit error
• EEPROM error
• CPU Internal A/D Converter Fault
• Perform an initialization to factory defaults.
• Cycle the Inverter power supply.
• Replace the Inverter.
CPF24
Option Comm Err
Hiperface serial communication error
Detected when no data were received from the
encoder for 200 msec
Check the encoder connection or replace the encoder
if necessary
DEV
Speed Deviation
F1-04 = 0, 1 or 2 and A1-02 = 3 or 6
The speed deviation is higher than the F1-10 value
for the time F1-11 or longer.
• Reduce the load.
• Lengthen the acceleration time and deceleration
time.
• Check the mechanical system.
• Check the settings of F1-10 and F1-11.
• Check the sequence and if the brake is opened when
the inverter starts to increase the speed.
F1-04 = 3 and A1-02 = 3 or 6
The speed deviation is higher than the F1-10 value
for the time F1-11 or longer.
DV3
Wrong rotation direction
Detected when the speed deviation is higher than
30% and the torque reference and acceleration have
opposite signs.
• Check the PG wiring
• Correct the wiring
• Verify the PG direction and execute an encoder off-
set auto tuning
• Reduce the load and check the brake
DV4
Wrong rotation direction
Detected when F1-19 is not 0, the speed reference
and motor speed have opposite signs and the detec-
tion threshold set in F1-19 is exceeded.
• Verify the PG direction and execute an encoder off-
set auto tuning
• Reduce the load and check the brake
DV6
Over Accelera-
tion
An over acceleration of the car was detected
(A1-02 = 6 only)
• Reduce the load
• Check the PG direction, check F1-22 and perform
an encoder offset tuning.
• Verify the settings of S3-13, S3-14 and S3-15.
• Adjust the acceleration and deceleration times.
EF0
Opt External Flt
External fault input from Communications Option
Card
• Check for an external fault condition.
• Verify the parameters.
• Verify communication signals
EF
Ext Fault S
External fault at terminal S
(
stands for terminals
S3 to S7)
Eliminate the cause of the external fault condition.
EF
External Fault
(flashing)
Forward/Reverse Run Commands Input Together
Both the forward and the reverse run commands are
input simultaneously for 500ms or more. This alarm
stops the motor.
Check external sequence logic, so that only one input
is received at a time.
Ext Run Active
Cannot Reset
Fault reset was tried during run.
• Remove the direction signal and retry a fault reset.
• If a PLC handles the fault reset, check the sequence.






















