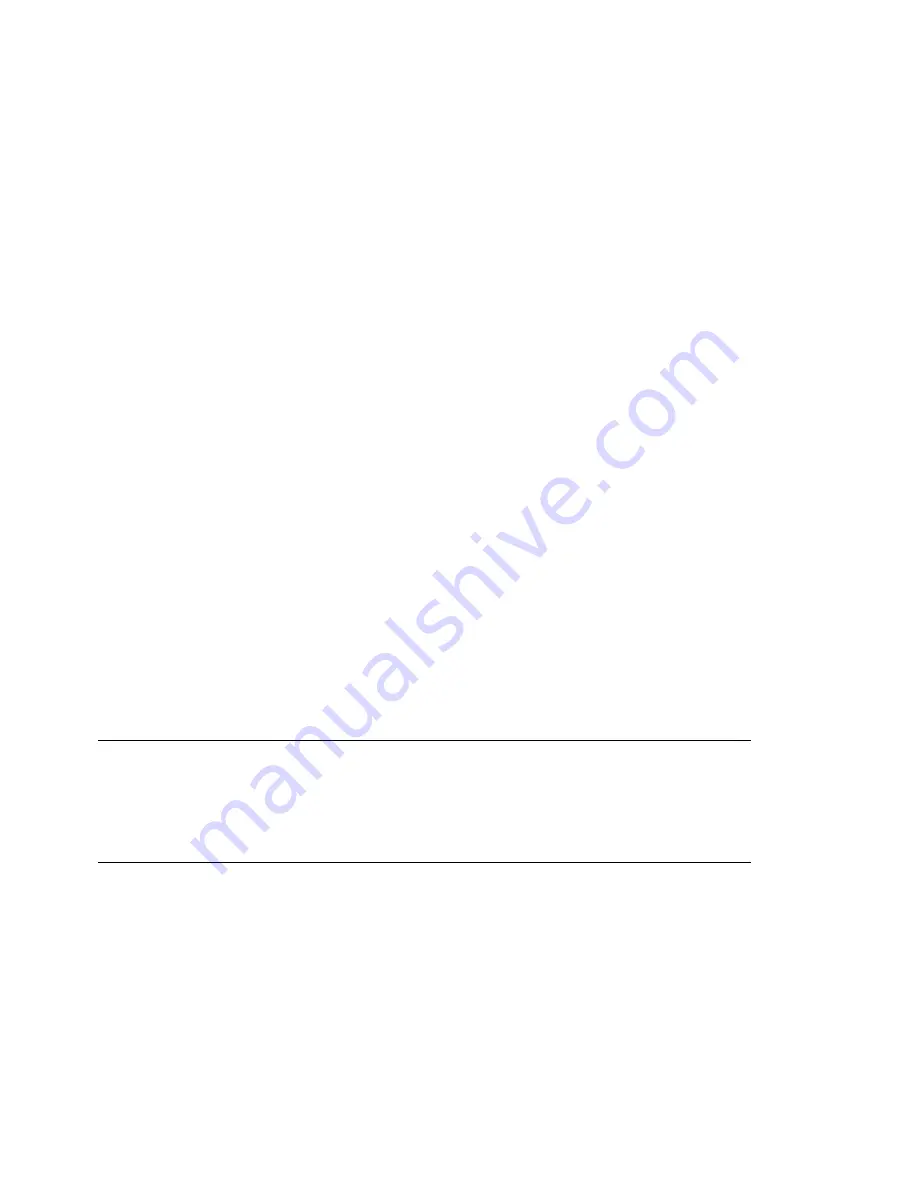
Example 2.1
An Example IOCDS
CHPID PATH=FD,TYPE=DSD,PART=(Z1)
CHPID PATH=FE,TYPE=OSA,PART=(Z1)
CHPID PATH=10,TYPE=CNC,PART=(Z1)
CNTLUNIT CUNUMBR=FD00,PATH=FD,UNITADD=((00,1)),UNIT=3990-2
IODEVICE ADDRESS=(FD00,1),CUNUMBR=FD00,UNIT=3390
CNTLUNIT CUNUMBR=FE20,PATH=FE,UNIT=OSA,UNITADD=((20,1))
IODEVICE ADDRESS=(FE20,1),CUNUMBR=FE20,UNIT=OSA,PART=Z1
CNTLUNIT CUNUMBR=100A,PATH=10,UNIT=3480,UNITADD=((0A,1))
IODEVICE ADDRESS=100A,CUNUMBR=100A,UNIT=3480,PART=Z1
Proceed with
Section 2.4.1, “LPAR Installation”
(page 19).
2.3.2 z/VM Installation
Adding a Linux Guest
The first step is to attach and format one or multiple DASDs in the system to be used
by the Linux guest in z/VM. Next, create a new user in z/VM. The example shows the
directory for a user
LINUX1
with the password
LINPWD
, 256 MB of memory (extend-
able up to 512 MB), 32 MB of expanded RAM (XSTORE), some minidisks (MDISK),
two CPUs and an OSA QDIO device.
TIP: Assigning Memory to z/VM guests
When assigning memory to a z/VM guest, make sure that the memory size suits
the needs of your preferred installation type. See
Section “Memory Require-
ments”
(page 2).
Preparing for Installation
17
















































