Nitto Construction
- 10 -
3. Index Values
3.1 Fundamental Principles
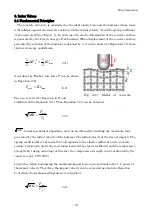
The concrete structure is considered as the ideal elastic body and the hammer whose mass
is
M
collides against the concrete surface with the initial velocity
V
and the spring coefficient
of the concrete
K
(See Fig 3.1-1). In such case the elastic deformation of the concrete surface
is generated by the kinetic energy of the hammer. When displacement of the concrete surface
generated by collision of the hammer is denoted by
x
, it can be shown in Equation (3.1) from
the law of energy equilibrium.
2
max
2
0
2
1
2
1
Kx
MV
(3.1)
According the Hooke’s law, force F can be shown
in Equation (3.2).
max
max
Kx
F
(3.2)
The
x
max
is solved by Equation (3.2) and
substituted into Equation (3.1). Thus, Equation (3.3) can be obtained.
0
max
V
F
MK
(3.3)
MK
means mechanical impedance and can be obtained by dividing the maximum force
generated by the initial velocity of the hammer (the initial velocity at the time of impact). The
spring coefficient K is the index that corresponds to the elastic coefficient on the concrete
surface. It is known about the correlation between the elastic coefficient and the compressive
strength. By taking advantage of this fact, the compressive strength can be estimated by the
concrete tester, CTS-02V4.
In practice, when hammering the maximum impact force is proportional to the 1. 2 power of
the impact velocity. Therefore, the impact velocity can be corrected as shown in Equation
(3.4) when the mechanical impedance is calculated.
2
.
1
0
max
V
F
MK
(3.4)
Fig 3.3-1 Model of concrete
Summary of Contents for CTS-02V4
Page 1: ...CTS 02V4 User Manual...