Connections for Multi-Gigabit Ethernet Throughput
13
ProSAFE Dual Band Wireless AC Access Point Model WAC740
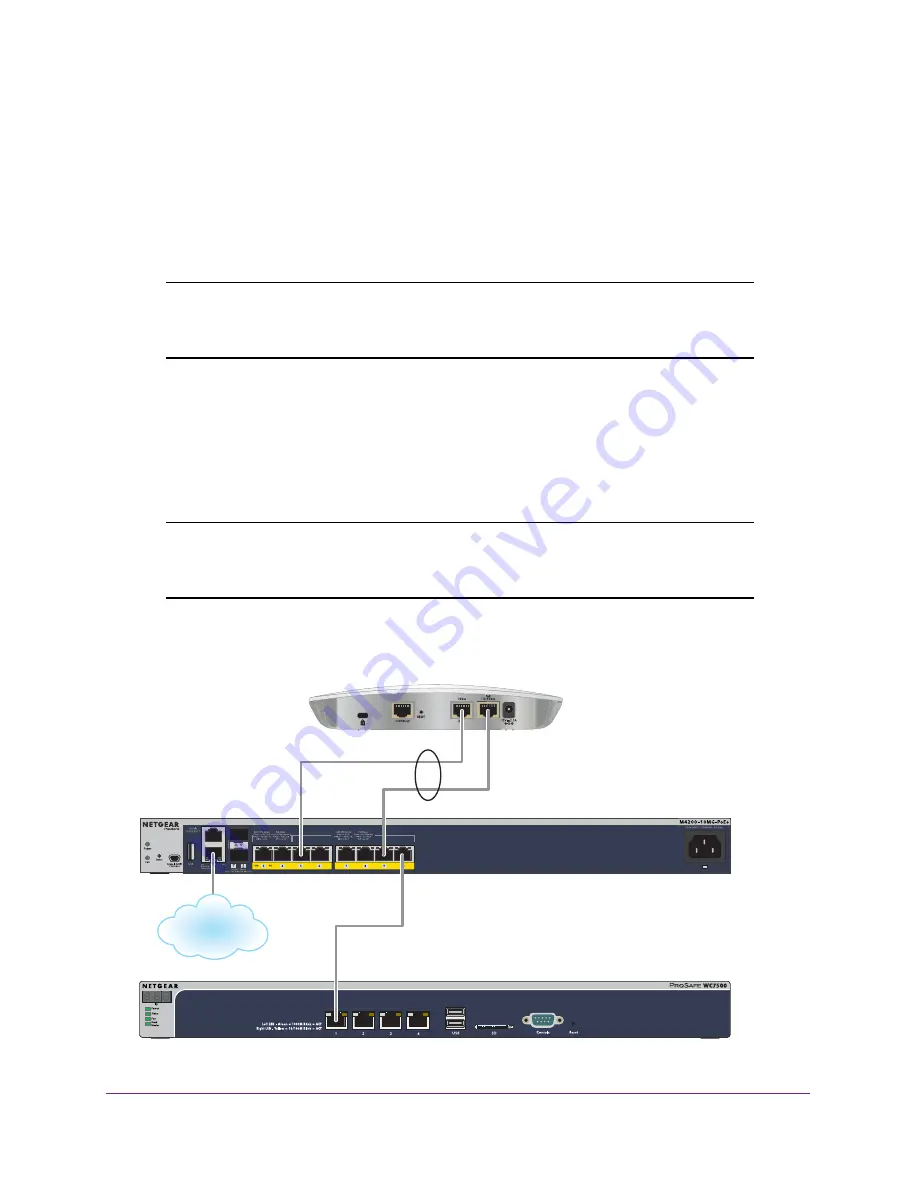
Static LAG Connection to a Switch
If your network does not include a switch with ports that provide multi-Gigabit Ethernet
throughput, connect the access point’s two LAN ports to a switch and set up a static link
aggregation group (LAG) that allows either a single 2 Gbps connection or a 1 Gbps
redundancy connection between the access point and the switch. The switch must support
static LAGs.
Note:
The access point supports a manual static LAG only. The access
point does not support IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation or Link
Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) groups.
When you set up a static LAG, the access point’s 2.5 Gbps Ethernet port (LAN port 1) is
limited to 1 Gbps and the total throughput of the LAG connection is 2 Gbps (LAN port 1
provides 1 Gbps and LAN port 2 provides 1 Gbps.) The LAG connection also provides
redundancy in case one of the LAN ports fails. For the LAG to function, you must enable the
LAG on the access point, configure a LAG for the access point on the switch, and configure a
LAG for the access point on the wireless controller.
Note:
The access point requires PoE+. PoE (802.3af) is not sufficient. If
your switch does not support PoE+ (802.3at), you can purchase a
NETGEAR power adapter for the access point.
For information about setting up a LAG connection, see
Option 2: Set Up a LAG Connection
to a Switch
on page 18.
Figure 5. LAG connection to an M4200 ProSAFE Managed Switch
Network core
Access point
Switch
Wireless controller
LAG














































