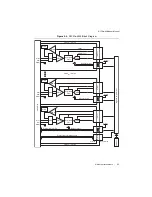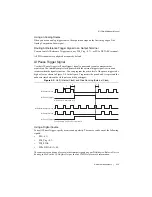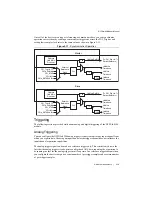
2-6
|
ni.com
Chapter 2
Using the NI PXIe-4300
Signal Acquisition Considerations
This section contains information about signal acquisition concepts including timing, triggering,
and synchronization.
Input Ranges
Input range refers to the set of input voltages that an analog input channel can digitize with the
specified accuracy. The programmable gain instrumentation amplifier (PGIA) amplifies or
attenuates the AI signal depending on the input range. You can individually program the input
range of each AI channel on your NI PXIe-4300 module.
The input range affects the resolution of the NI PXIe-4300 module for an AI channel. Resolution
refers to the voltage of one ADC code. For example, a 16-bit ADC converts analog inputs into
one of 65,536 (= 2
16
) codes—that is, one of 65,536 possible digital values. These values are
spread fairly evenly across the input range. So, for an input range of -10 V to 10 V, the voltage
of each code of a 16-bit ADC is:
Choose an input range that matches the expected input range of your signal. A large input range
can accommodate a large signal variation, but reduces the voltage resolution. Choosing a smaller
input range improves the voltage resolution, but may result in the input signal going out of range.
Note
The NI PXIe-4300 module uses a calibration method that requires codes
(typically about 5% of the codes) outside of the specified range. This calibration
method improves absolute accuracy, but it decreases the nominal resolution of input
ranges by about 5% over what the formula shown above would indicate.
Table 2-3 shows the input ranges and resolutions supported by the NI PXIe-4300 module.
Table 2-3.
NI PXIe-4300 Input Range and Nominal Resolution
Input Range
Nominal Resolution Assuming 5% Over Range
-10 V to 10 V
320
μ
V
-5 V to 5 V
160
μ
V
-2 V to 2 V
64
μ
V
-1 V to 1 V
32
μ
V
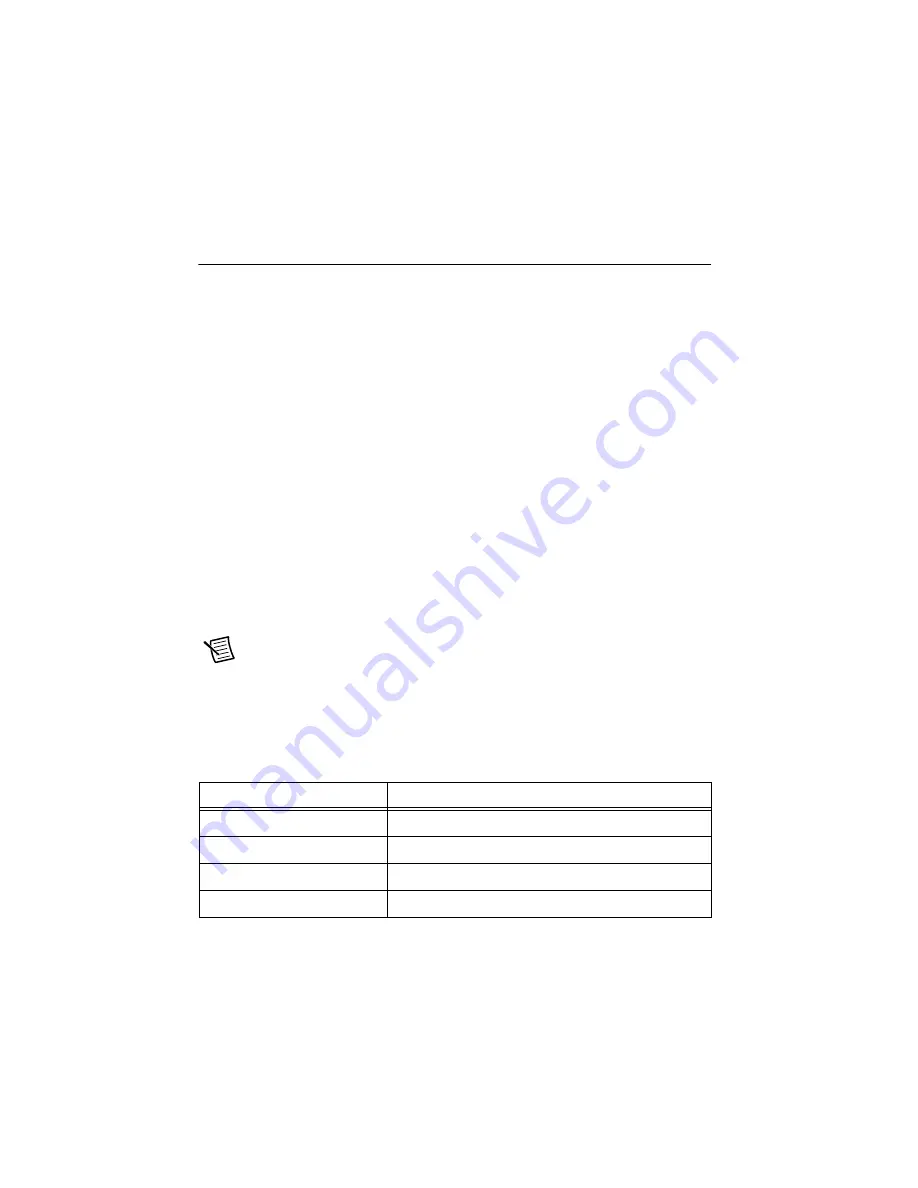
10 V (–10 V)
–
2
16
------------------------------------
305
μ
V
=