Page 75
Appendix | EtherCAT Documentation
optoNCDT 1900 / EtherCAT
A 5.2
Introduction
A 5.2.1
Structure of EtherCAT® Frames
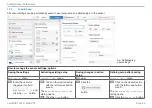
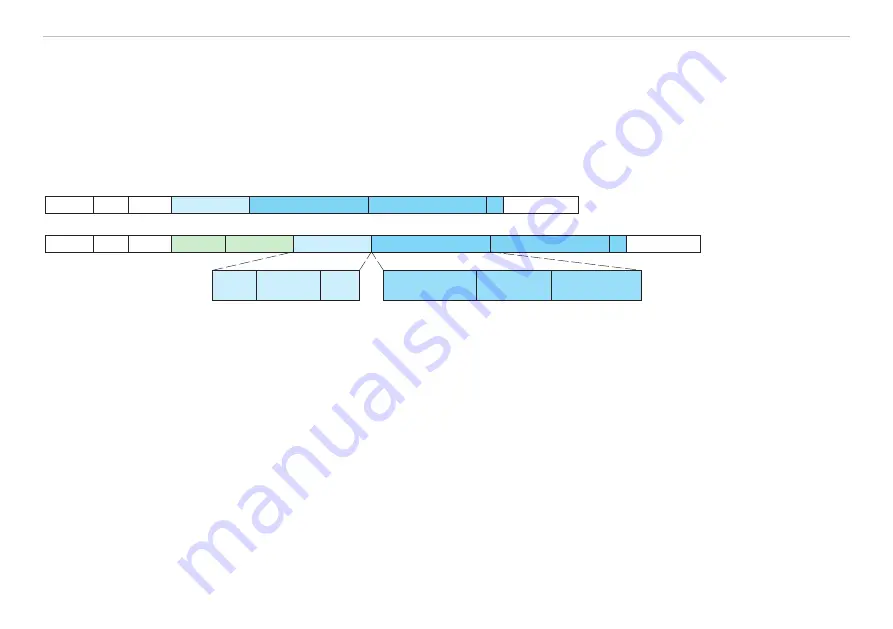
The transfer of data occurs in Ethernet frames with a special Ether type (0x88A4). Such an EtherCAT® frame consists of one or
several EtherCAT® telegrams, each of which is addressed to individual slaves / storage areas. The telegrams are either transmitted
directly in the data area of the Ethernet frame or in the data area of the UDP datagram. An EtherCAT® telegram consists of an Ether-
CAT® header, the data area and the work counter (WC). The work counter is incremented by each addressed EtherCAT® slave that
exchanged the corresponding data.
Ethernet frame 0x88A4
ODER
UDP/IP 0x88A4
Destination Source EtherType
Destination Source EtherType
1. EtherCAT datagram 2. EtherCAT datagram
...
Ethernet-CRC
Frame header
1. EtherCAT datagram 2. EtherCAT datagram
...
EtherCAT header
(10 byte)
Data
(min 32 byte)
Working counter
(2 byte)
Length
(11 bit)
Resolution
(1 bit)
Type
(4 bit)
Ethernet-CRC
Frame header
IP header UDP header
Fig. 32 Setup of EtherCAT frames
A 5.2.2
EtherCAT® Services
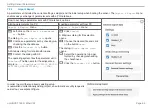
EtherCAT® services specify the reading and writing of data in the physical memory of the slave hardware. The following EtherCAT®
services are supported by the slave hardware:
- APRD (Auto-Increment Physical Read, reading of a physical area with auto-increment addressing)
- APWR (Auto-Increment Physical Write, writing of a physical area with auto-increment addressing)
- APRW (Auto-Increment Physical Read Write, reading and writing of a physical area with auto-increment addressing)
- FPRD (Configured Address Read, reading of a physical area with fixed addressing)
- FPWR (Configured Address Write, writing of a physical area with fixed addressing)
- FPRW (Configured Address Read Write, reading and writing of a physical area with fixed addressing)
- BRD (Broadcast Read, broadcast-reading of a physical area for all slaves)
- BWR (Broadcast Write, broadcast-writing of a physical area for all slaves)
- LRD (Logical Read, reading of a logical storage area)
- LWR (Logical Write, writing of a logical storage area)
- LRW (Logical Read Write, reading and writing of a logical storage area)
- ARMW (Auto-Increment Physical Read Multiple Write, reading of a physical area with auto-increment addressing, multiple writing)
Summary of Contents for ILD1900-10
Page 8: ...optoNCDT 1900 EtherCAT ...
Page 110: ...Page 110 Appendix EtherCAT Documentation optoNCDT 1900 EtherCAT ...
Page 111: ......