800.MACTOOLS
39
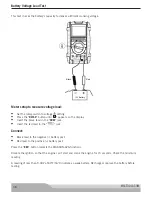
Voltage Load Test Battery Voltage Vs Battery/Air Temperature
Meter Reading
Battery/Air Temperature
10.0V
90°F/33°C
9.8V
80°F/27°C
9.6V
70°F/21°C
9.4V
60°F/16°C
9.2V
50°F/10°C
9.0V
40°F/4°C
8.8V
30°F/-1°C
8.6V
20°F/-7°C
NOTE:
The above table is only for non-critical reference.
Battery temperature can be checked by using the meter’s temperature function.
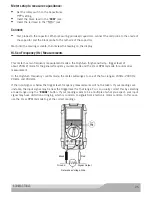
VOLTAGE DROP TESTS
Voltage drop tests measure the amount of voltage expended to overcome resistance (an opposing force to
the flow of electrical current created by a circuit or component); the lower the voltage drop reading, the less
resistance in the circuit under test.
The Hold function and the MAX/MIN Record function are very useful for measuring voltage drops on many
different components and connections. For example, measuring the voltage drop across the connections and
components in the starter circuit while cranking the engine (ignition or fuel system disabled to prevent starting)
allows you to determine if there is excess resistance in the starter circuit.
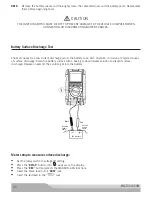
To measure voltage drop, current must be flowing in the circuit and both voltage test probes must be connected
on the same side of the circuit. Voltage drop can also be determined from available voltage readings by noting
the difference between each successive reading.
Refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s specification for voltage drop information. If the voltage drop specification
is not available, refer to the following table to determine typical voltage drop for 12V systems:
Typical Allowable Voltage Drop
Component
Typical Voltage Drop
Battery cable length up to 3 feet
0.1V
Battery cable length over 3 feet
0.2V
Magnetic switches
0.3V
Solenoid switches
0.2V
Mechanical switches
0.1V
Battery cable connectors
0.05V
Connections
0.0V