Appendix C Configuring In-Band Management
Using the Routed Connection Configuration
C-4
255-700-025
PacketStar
™
Access Concentrator 60 User Guide
, Issue 1
Release 6.3.0
AAL= 5
Check whether the connections have been configured by using the
command
atmarp -a
2
All the remote PSAX systems’ in-band interface IP addresses may or may
not be in the same subnet as that of the FORE card’s IP address.
3
If the remote PSAX systems’ in-band interface IP address is not in the
same subnet as that of the FORE card’s IP address, then a route entry
should be added on the SUN machine for the remote PSAX systems’
subnet, using the FORE card interface as the gateway.
4
On the PSAX system, the in-band management interface (primary)
should be assigned an IP address that lies in a different network than
that of its Ethernet interface.
5
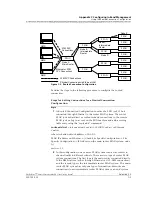
The in-band connection from each of the remote PSAX systems is a
direct connection to the SUN machine’s FORE card interface IP address.
(Here a direct connection implies that it should not be IP routed through
a CPU module. It should be an ATM connection, which may be tunneled
through a number of switches.)
6
If the ATM end points are connected to a Cisco router instead of a SUN
machine, then the remote PSAX system can be configured with a default
gateway address, which should be the same as the in-band connection
end point’s IP address (that is, the Cisco router’s address).
7
The gateway IP address should be either an Ethernet subnet or an in-
band management subnet. The gateway IP address should not be the
same as the in-band IP address.
8
If the gateway IP address is in the in-band management subnet, then
there should be an in-band connection to that address.
9
If a traffic-shaping OC-3 card is used, the recommended values for in-
band connection are Peak Rate: 2000 cps; Sustained Rate: 1000 cps;
MBS: 10000 cells.
End
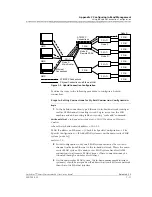
Using the Routed Connection Configuration
No default gateway through an in-band network should be configured on
any of the PSAX systems.