24
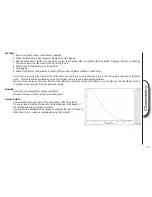
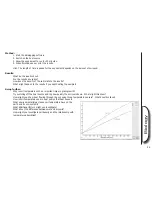
Cooling curves
Subject: Chemistry
Sensor: Temperature
Aim:
To show the technique for recording a cooling curve and subsequent freezing point for tap, distilled and salty water.
Overview:
A change of state is a change from one physical state to another eg. solid to liquid or liquid to gas. While this change of state is occurring, there is no
change in temperature as all of the energy is used to make or break molecular bonds. In practice this can be quite difficult to show.
Equipment required:
LogIT Black Box
Temperature sensor
Small vessel, beaker or boiling tube
Freezer
Salt (Sodium Chloride)
Tap water (No hotter than 40
O
C)
Distilled water (No hotter than 40
O
C)
Hazards:
If warming the water first, make sure the water is not too hot for the ability of the students. Water
temperature above 55
o
C will scold Students. It is sometimes useful to use hot water from the
schools water supply.
Care must be taken if using kettles to heat the water. Allow the temperature to cool before use.
To avoid cross contamination, do not use a freezer which contains food for human consumption.
Do not put very hot water into a freezer as damage to the freezer may result.
Setup:
1. Connect the Temperature sensor to Black Box and then connect Black Box to the computer.
2. Start the logging software.
2. Place the water into the small vessel, beaker or boiling tube.
Note: For good results it is necessary to make sure that the Temperature probe does not touch the sides of the container. This can be
achieved either by passing the probe through thick card and suspend the probe in the middle of the water or by carefully ‘hooking’ the
probe on the edge of the vessel using the probe’s cable. (Do not bend the cable at a tight angle as this can damage the cable)