12
LTC3729
sn3729 3729fas
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
W
U
U
U
When using the controller in very low dropout conditions,
the maximum output current level will be reduced due to
internal slope compensation required to meet stability
criterion for buck regulators operating at greater than 50%
duty factor. A curve is provided to estimate this reduction
in peak output current level depending upon the operating
duty factor.
Operating Frequency
The LTC3729 uses a constant frequency, phase-lockable
architecture with the frequency determined by an internal
capacitor. This capacitor is charged by a fixed current plus
an additional current which is proportional to the voltage
applied to the PLLFLTR pin. Refer to Phase-Locked Loop
and Frequency Synchronization in the Applications Infor-
mation section for additional information.
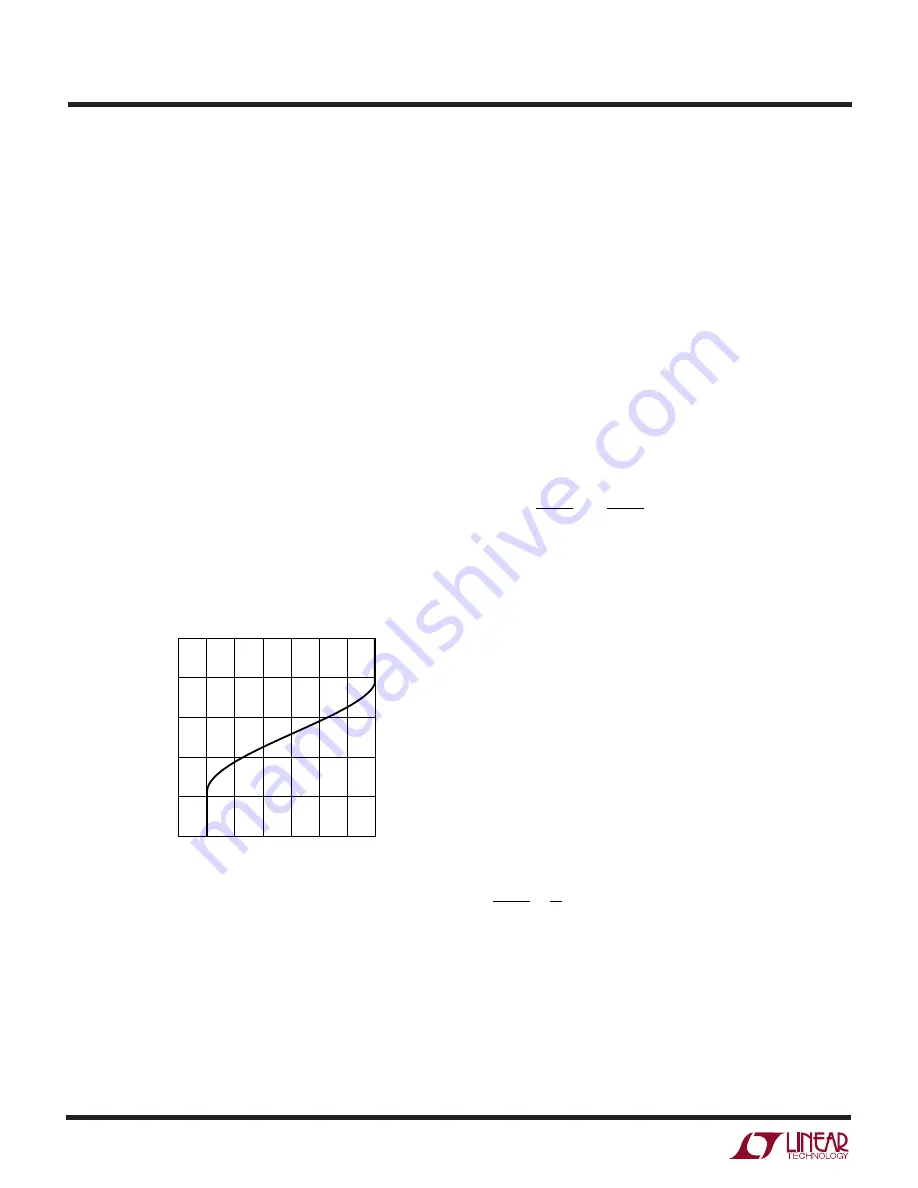
A graph for the voltage applied to the PLLFLTR pin vs
frequency is given in Figure␣ 2. As the operating frequency
is increased the gate charge losses will be higher, reducing
efficiency (see Efficiency Considerations). The maximum
switching frequency is approximately 550kHz.
anyone ever choose to operate at lower frequencies with
larger components? The answer is efficiency. A higher
frequency generally results in lower efficiency because of
MOSFET gate charge and transition losses. In addition to
this basic tradeoff, the effect of inductor value on ripple
current and low current operation must also be consid-
ered. The PolyPhase approach reduces both input and
output ripple currents while optimizing individual output
stages to run at a lower fundamental frequency, enhancing
efficiency.
The inductor value has a direct effect on ripple current. The
inductor ripple current
∆
I
L
per individual section, N,
decreases with higher inductance or frequency and in-
creases with higher V
IN
or V
OUT
:
∆
I
V
fL
V
V
L
OUT
OUT
IN
=
−
1
where f is the individual output stage operating frequency.
In a PolyPhase converter, the net ripple current seen by the
output capacitor is much smaller than the individual
inductor ripple currents due to the ripple cancellation. The
details on how to calculate the net output ripple current
can be found in Application Note 77.
Figure 3 shows the net ripple current seen by the output
capacitors for the different phase configurations. The
output ripple current is plotted for a fixed output voltage as
the duty factor is varied between 10% and 90% on the
x-axis. The output ripple current is normalized against the
inductor ripple current at zero duty factor. The graph can
be used in place of tedious calculations. As shown in
Figure␣ 3, the zero output ripple current is obtained when:
V
V
k
N
OUT
IN
=
where k = 1, 2, …, N – 1
So the number of phases used can be selected to minimize
the output ripple current and therefore the output ripple
voltage at the given input and output voltages. In applica-
tions having a highly varying input voltage, additional
phases will produce the best results.
Figure 2. Operating Frequency vs V
PLLFLTR
OPERATING FREQUENCY (kHz)
200
250
300
350
550
400
450
500
PLLFLTR PIN VOLTAGE (V)
3729 F02
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
Inductor Value Calculation and Output Ripple Current
The operating frequency and inductor selection are inter-
related in that higher operating frequencies allow the use
of smaller inductor and capacitor values. So why would