14
LTC3729
sn3729 3729fas
P
V
V
I
N
R
k V
I
N
C
f
MAIN
OUT
IN
MAX
DS ON
IN
MAX
RSS
=
+
( )
+
( )
( )( )
2
2
1
δ
(
)
P
V
V
V
I
N
R
SYNC
IN
OUT
IN
MAX
DS ON
=
+
( )
–
(
)
2
1
δ
where
δ
is the temperature dependency of R
DS(ON)
, k is a
constant inversely related to the gate drive current and N
is the number of stages.
Both MOSFETs have I
2
R losses but the topside N-channel
equation includes an additional term for transition losses,
which peak at the highest input voltage. For V
IN
< 20V the
high current efficiency generally improves with larger
MOSFETs, while for V
IN
> 20V the transition losses rapidly
increase to the point that the use of a higher R
DS(ON)
device
with lower C
RSS
actual provides higher efficiency. The
synchronous MOSFET losses are greatest at high input
voltage when the top switch duty factor is low or during a
short-circuit when the synchronous switch is on close to
100% of the period.
The term (1 +
δ
) is generally given for a MOSFET in the
form of a normalized R
DS(ON)
vs. Temperature curve, but
δ
= 0.005/
°
C can be used as an approximation for
low voltage MOSFETs. C
RSS
is usually specified in the
MOSFET characteristics. The constant k = 1.7 can be used
to estimate the contributions of the two terms in the main
switch dissipation equation.
The Schottky diodes, D1 and D2 shown in Figure 1 conduct
during the dead-time between the conduction of the two
large power MOSFETs. This helps prevent the body diode
of the bottom MOSFET from turning on, storing charge
during the dead-time, and requiring a reverse recovery
period which would reduce efficiency. A 1A to 3A (depend-
ing on output current) Schottky diode is generally a good
compromise for both regions of operation due to the
relatively small average current. Larger diodes result in
additional transition losses due to their larger junction
capacitance.
C
IN
and C
OUT
Selection
In continuous mode, the source current of each top
N-channel MOSFET is a square wave of duty cycle V
OUT
/
V
IN
. A low ESR input capacitor sized for the maximum
RMS current must be used. The details of a close form
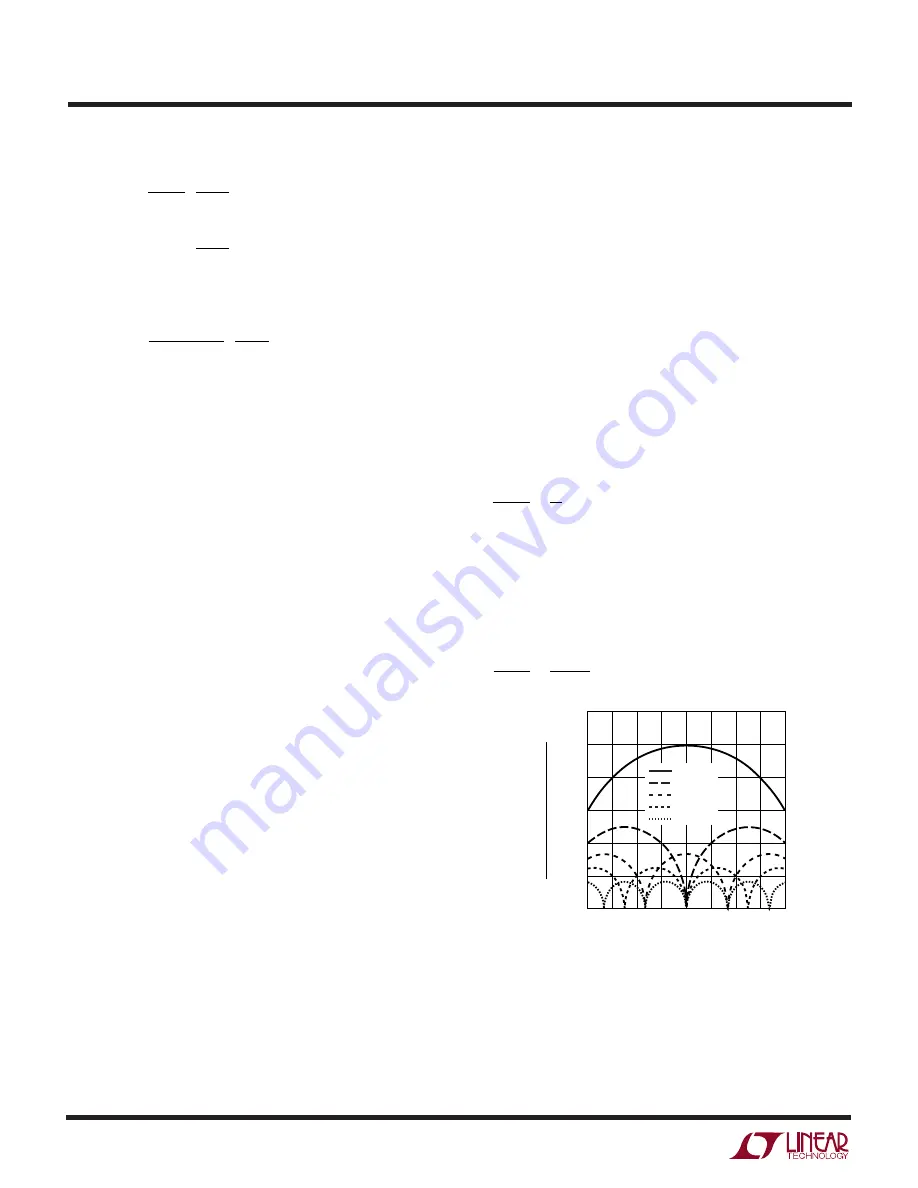
equation can be found in Application Note 77. Figure 4
shows the input capacitor ripple current for different
phase configurations with the output voltage fixed and
input voltage varied. The input ripple current is normalized
against the DC output current. The graph can be used in
place of tedious calculations. The minimum input ripple
current can be achieved when the product of phase num-
ber and output voltage, N(V
OUT
), is approximately equal to
the input voltage V
IN
or:
V
V
k
N
OUT
IN
=
where k = 1, 2, …, N – 1
So the phase number can be chosen to minimize the input
capacitor size for the given input and output voltages.
In the graph of Figure 4, the local maximum input RMS
capacitor currents are reached when:
V
V
k
N
OUT
IN
=
−
2
1
2
where k = 1, 2, …, N
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
W
U
U
U
Figure 4. Normalized Input RMS Ripple Current vs
Duty Factor for 1 to 6 Output Stages
DUTY FACTOR (V
OUT
/V
IN
)
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
3729
F04
RMS INPUT RIPPLE CURRNET
DC LOAD CURRENT
6-PHASE
4-PHASE
3-PHASE
2-PHASE
1-PHASE
These worst-case conditions are commonly used for
design because even significant deviations do not offer
much relief. Note that capacitor manufacturer’s ripple
current ratings are often based on only 2000 hours of life.














































