60
Copyright © 2000 - 2005 KEMP Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
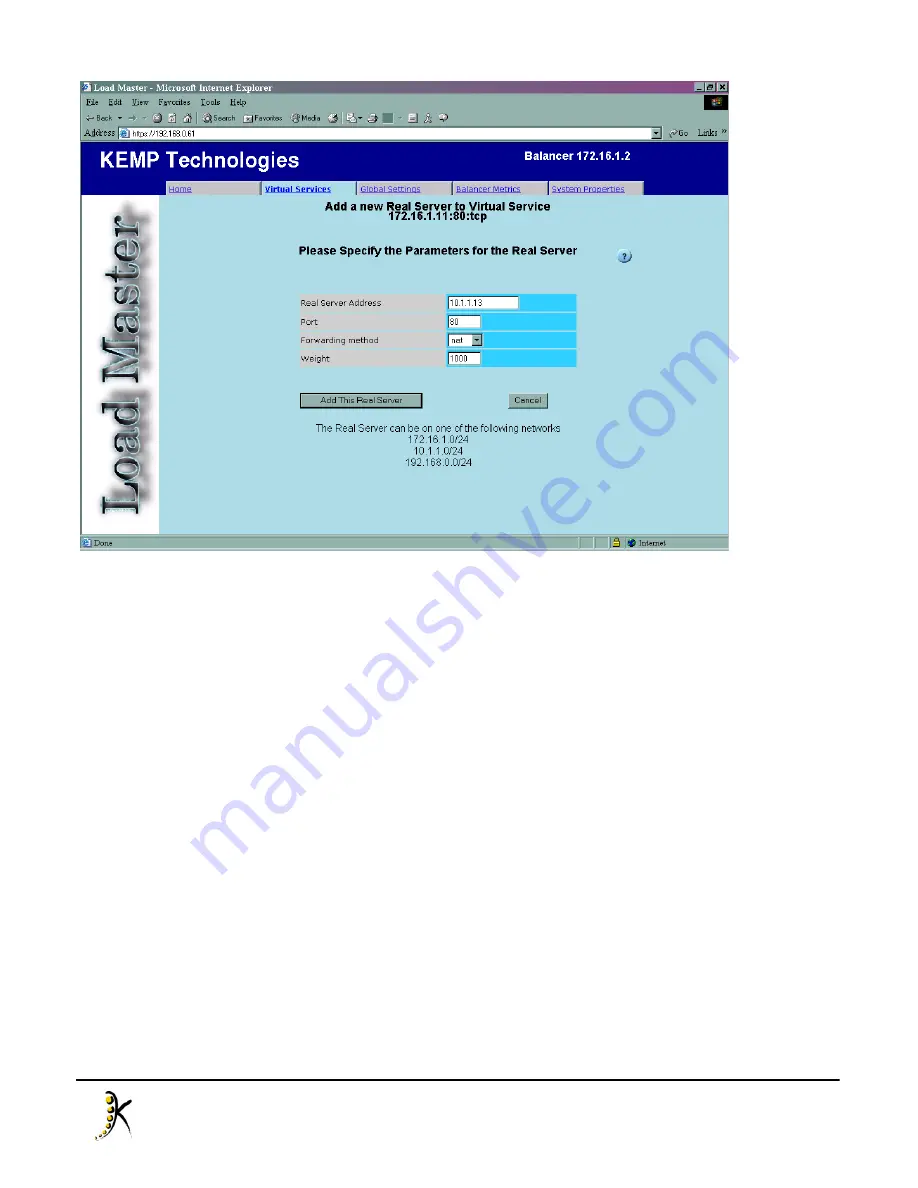
In our example, we will assume that the real servers are on a private 10.1.1.x network, and we will then enter
real server 10.1.1.13. At this stage, we do not need to worry about the port, forwarding method and weight.
Click “Add This Real Server” to finish.
The virtual service properties page should now display the recently added real server in the real server table.
To add another real server, repeat the process but with a different real server IP address.
All changes are made in real-time, so we have now created the virtual service. To return to the virtual service
page, either click “Virtual Services” link at the top-left of the frame, or click the “Virtual Services” tab. The
virtual service table should now list the service we have just created.
3. Create a Virtual Service with Content Rules
This section will take you through the steps required to set up a virtual service that makes use of content
switching. Content Switching means that the Balancer can distribute requests to a server depending on the
content of the request.
To begin with, we need to create at least one content rule. It usually makes sense to create more rules. The
content rule management section of the WUI is found under the “Global Settings” tab. Clicking on this tab
brings up the “Content Rule Management” section as default. This section consists of a summary list of
content rules, if they exist.












































