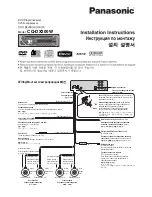
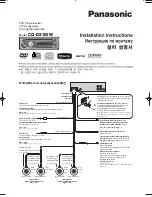
Transmitter Description
User Manual
47
STEL-2176
Symbol Mapper
The Symbol Mapper receives I
1
*
, Q
1
*
, I
0
*
, Q
0
*
of each
symbol. Based on the signal modulation and the symbol
mapping selection, the Symbol Mapper block maps the
symbol to a constellation data point (I
1
,Q
1
,I
0
,Q
0
). The
Symbol Mapping field (bits 7-5 of Block 2 Register 2E
H
)
will map the four input bits to a new value, as indicated
in Table 41.
BPSK and QPSK
For BPSK and QPSK, the settings of the symbol to
constellation mapping bits is ignored. The
constellations for BPSK (Figure 29) and QPSK (Figure
30) are shown below. I
1
Q
1
values are indicated by large,
bold font (
00
and
11)
and I
0
Q
0
values by the smaller
font (00 and 11).
16
QAM
For 16QAM modulation, the Symbol Mapper maps
each input symbol to one of the 16QAM constellations.
The specific constellation is programmed by the Symbol
Mapping field (bits 7-5 of Block 2 Register 2E
H
) to select
the type of symbol mapping. If the MSB of the Symbol
Mapping field is set to 0, the mapping will be bypassed
and I
1
Q
1
I
0
Q
0
= I
1
*
Q
1
*
I
0
*
Q
0
*
. The resulting constellation
(Figure 31) is the natural constellation for the
STEL-2176.
If the MSB of the Symbol Mapping field is set to 1, bits
6-5 can select any of four possible types of symbol
mapping (Gray, DAVIC, Left, or Right), as indicated by
Table 41.
Table 42 summarizes the symbol mapping and the
resulting constellations are shown in Figure 31 and
Figure 32. In these figures, I
1
Q
1
are indicated by large,
bold font (
00, 01, 10,
a n d
11)
and I
0
Q
0
by the
smaller font (00, 01, 10, and 11).
00
11
00
11
1
3
-1
-3
-3
-1
1
3
Q
I
WCP 52999.c-10/29/97
Figure 29. BPSK Constellation
1
3
-1
-3
-3
-1
1
3
00
10
01
11
Q
I
00
10
11
01
WCP 52986.c-10/29/97
Figure 30. QPSK Constellation