Application Note
6 of 53
V 1.0
2019-04-01
IM393 Application note
IM393 IPM Technical Description
Internal components and package technology
2
Internal components and package technology
2.1
Power transistor and diode technology
IM393-XX IPM products are based on new Infineon IGBT6 TRENCHSTOP
™
technology [1]. This new IGBT
generation is based on trench and field-stop technology, and offers significant improvements in terms of loss
reduction. It features the well-known properties of robustness of Infineon’s IGBT, including short-circuit-
withstand capability and maximum-junction temperature. Moreover, all the advantages of this technology are
maintained in order to achieve the highest efficiency and power density. The features include very low static
parameters such as the saturation voltage of the IGBT or the forward voltage of the diode. Excellent dynamic
parameters such as turn-off energy of the IGBT or the reverse-recovery charge of the diode are also valuable
features. The forward diodes are ultrafast with very soft recovery characteristics that lead to a reduction in
reverse-recovery and turn-on energy losses.
2.2
Control IC – Six-channel gate driver IC
The driver is a high-voltage, high-speed IGBT gate driver with three high-side and three low-side referenced
output channels for three-phase applications. The IC is designed to be used with low-cost bootstrap power
supplies. The bootstrap diode functionality has been integrated into this device to reduce the component
count on the PCB. Proprietary HVIC and latch-up immune CMOS technologies have been implemented in a
rugged monolithic structure. The floating logic input is compatible with standard CMOS and LSTTL output
(down to 3.3 V logic). A current-trip function which terminates all six outputs can be done by an external current
sense resistor. Enable functionality is available to terminate all six outputs simultaneously. An open-drain
FAULT signal is provided to indicate that a fault has occurred. Fault conditions are cleared automatically after a
delay programmed externally via an RC network connected to the RCIN input. The output drivers feature a
high-pulse current buffer stage designed for minimum driver cross conduction. Shoot-through protection
circuitry and a minimum dead-time circuitry have been integrated into this IC. Propagation delays are matched
to simplify the HVIC’s use in high-frequency applications.
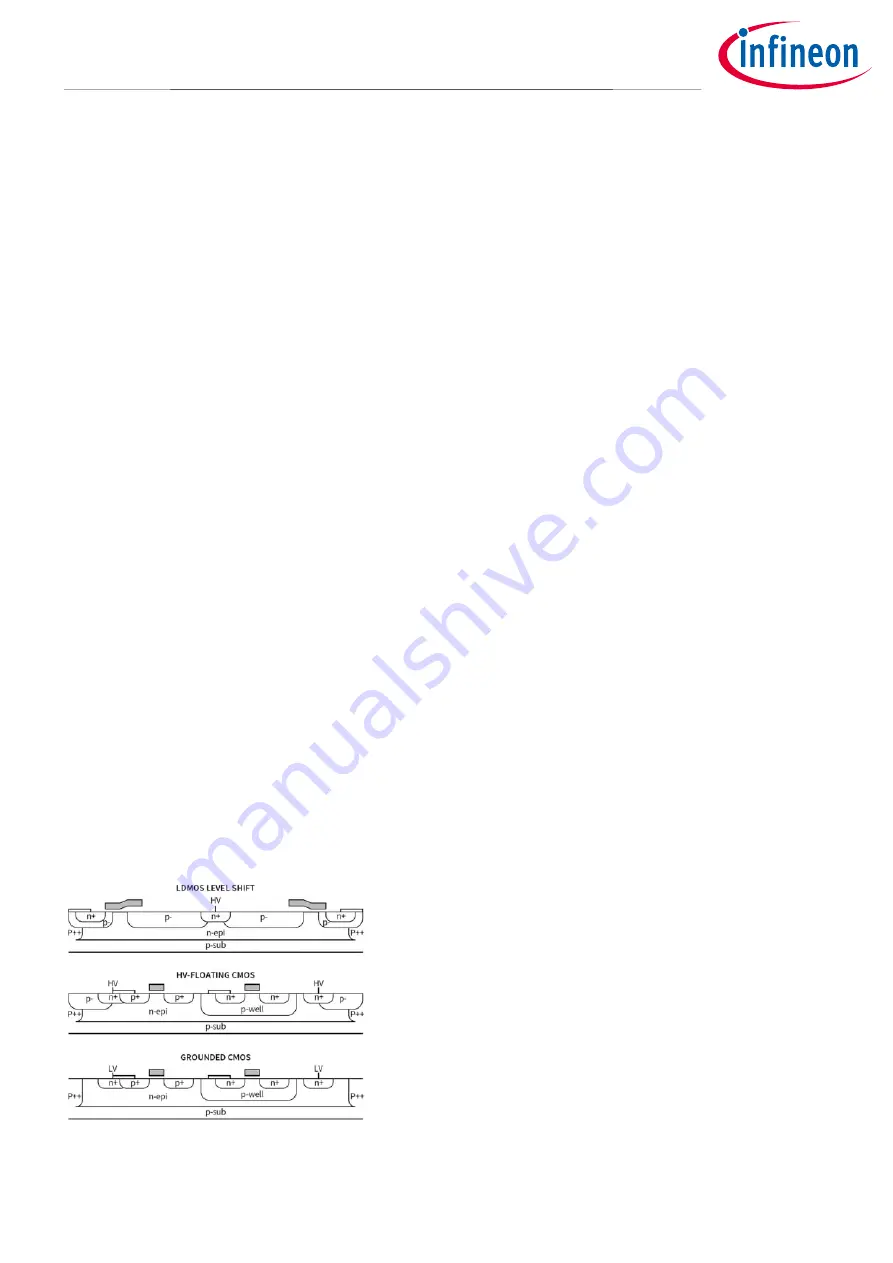
The HVIC technology uses proprietary monolithic structures integrating bipolar, CMOS and lateral DMOS
devices [2]. Using this mixed-signal HVIC technology, both high-voltage, level-shifting circuits, and low-voltage
analog and digital circuits can be implemented. This technology places high-voltage circuits in a ‘well’ formed
by polysilicon rings which can float 600 V within the same silicon, away from the low-voltage circuitry, as shown
in Figure 1.
These HVIC gate drivers with floating switches are well-suited for topologies requiring high-side and bridge
configuration.
Figure 1
Structure and cross section of the HVIC







































