Application Note
16 of 23
V 1.1
2020-11-09
CoolGaN™ 600 V half-bridge evaluation platform featuring GaN
EiceDRIVER™
Setup and use
4.8
Initial checkout
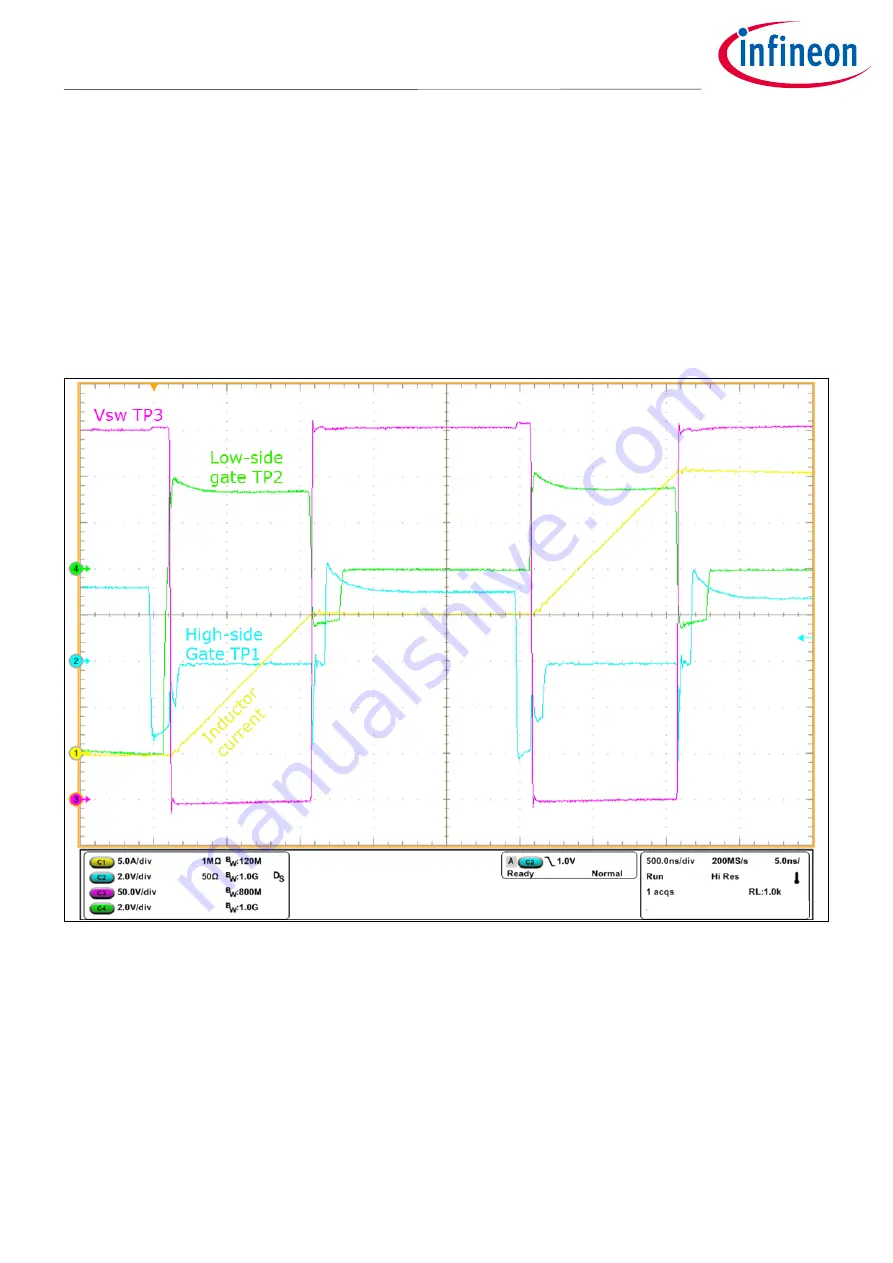
Assuming the board is already setup per section 4.6, the next step is to add an external inductor and bring-up
the DC bus to operate at the desired test condition. This example shows how to setup the board for double-
pulse testing. In double-pulse testing, first the half-bridge turns on and ramps-up inductor current to a test
value. Then the primary switch turns-off, and the current freewheels through the other device, which acts as a
synchronous rectifier. The second pulse shows hard-switched turn-on performance on the leading-edge (at the
test current) and then continues the ramp to a higher current level. GaN devices perform particularly well on
these tests because the freewheeling diode has zero reverse-recovery characteristic. Double –pulse testing is
typically done 1 burst at a time (not continuously) in order to keep power dissipation low, even when testing to
the voltage and current limits of the device.
Figure 14
Double-pulse test waveform example
Connect the external 25 µH inductor and HV power supply as shown in
. Set the pulse generator for a
pulse-width of 1 µs, and a period of 2.5 µs. setup a 2-pulse burst (refer to
). It is recommended to set
the pulse generator for manual mode, where each pulse set is triggered by a button-push.
Note:
When the low-side switch is operated in the double-pulse test, the default state of the half-bridge
is that the high-side synchronous rectifier is normally ON. Thus the logic input should be inverted –
normally high with two pulses going low. Make sure to power-off the HV supply before shutting-off
the output of the pulse generator: if the pulse generator is powered-off first, it will turn-on the low-
side and ramp the current to uncontrolled value, unless the bus is at zero volts.






















