Application Note
14 of 23
V 1.1
2020-11-09
CoolGaN™ 600 V half-bridge evaluation platform featuring GaN
EiceDRIVER™
Setup and use
limited to 0.2 A because the on-board bus capacitors will provide the peak current (for low-value inductors
<100 µH).
4.6
Verifying and adjusting deadtime
The evaluation board has two independent deadtime adjustments. When the PWM input goes high, the low side
gate driver turns off and then the high-side gate driver turns on after the rising-edge deadtime. This deadtime is
adjusted with the trim potentiometer R11. On the falling-edge of PWM input, the high-side gate driver turns off,
then the low-side gate driver turns on after the falling-edge deadtime. This is adjusted with the trim
potentiometer R21. You will need a small (1.2 mm) slotted (flat-blade) screwdriver to andjust the trimpots.
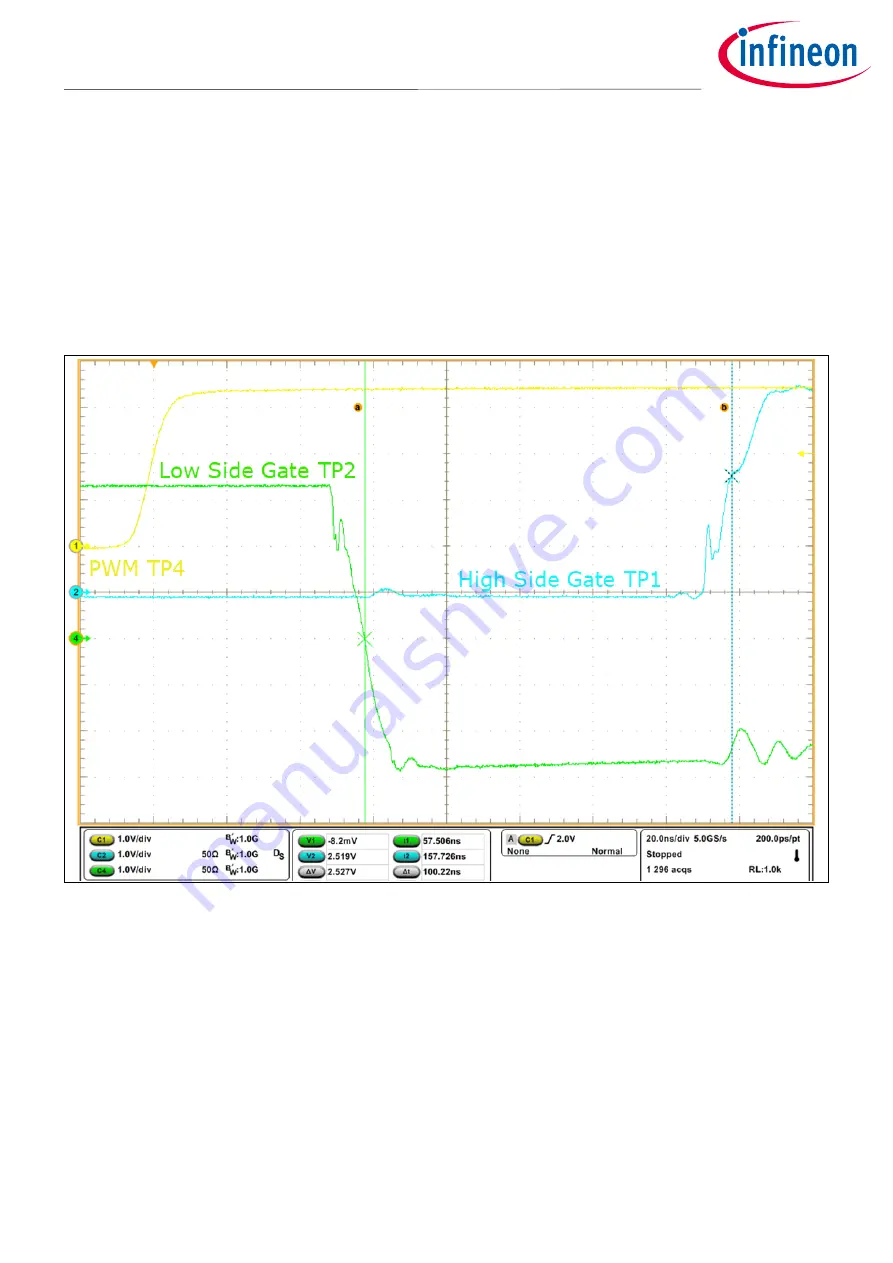
Figure 12
Measuring deadtime on the rising edge of PWM
To verify and adjust deadtime, connect a 5 V DC supply to the 5 V input on the eval board, and connect a pulse
generator to the PWM input J1 (refer to section 4.3). Set the generator for a square-wave (50 percent duty-cycle)
at 100 kHz and apply the 5 V power to the board. Connect an oscilloscope to TP4 as the reference PWM input.
Connect a probe to TP2 (low-side gate), and an isolated probe (TIVM1 mentioned earlier) to the high-side gate
test connector TP1. Be sure to follow the scope instructions for adjusting the scope channel timing-offset “de-
skew” values to compensate for the group delay of each probe. Isolated probes can have significant delay times
on the order of 30 ns, so that could result in a large error if the de-skew is not properly calibrated on the scope.
Note:
If isolated probe is not available, standard passive probes can be used to measure the high-side
gate signal for setting deadtime, as long as the high voltage bus is at 0 V. Just be sure to
disconnect the passive probe from TP1 before applying any bus voltage.























