HUAWEI HG655a Home Gateway
User Guide
Appendix
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8-1
8.3 Glossary
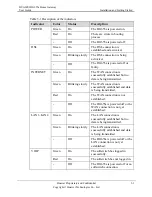
ACS
Automatic Configuration Server
A Web-based management system encompassing configuration and administration of an
end-to-end IP communications solution.
On your automatic-configuration server, create
global groups that correspond to your .ins file name (without the extension). For example,
IE_groupname.
ADSL
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
ADSL is a technology for transmitting digital information at a high bandwidth on
existing phone lines to homes and businesses. Unlike regular dial-up phone service,
ADSL provides continuously-available, "always on" connection. ADSL is asymmetric in
that it uses most of the channel to transmit downstream to the user and only a small part
to receive information from the user. ADSL simultaneously accommodates analog
(voice) information on the same line. ADSL is generally offered at downstream data
rates from 512 kbit/s to about 6 Mbit/s.
ADSL2+
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line 2+
ADSL2plus doubles the bandwidth used for downstream data transmission, effectively
doubling the maximum downstream data rates, and achieving rates of 20 Mbit/s on
phone lines as long as 5,000 feet. ADSL2plus solutions will most commonly be
multimode, interoperating with ADSL and ADSL2, as well as with ADSL2plus chipsets.
VDSL2
Very
High Speed Digital Subscribe Line 2
VDSL2 is an access technology that exploits the existing infrastructure of copper wires
that were originally deployed for POTS. It can be deployed from central offices, from
fibre-fed cabinets located near the customer premises, or within buildings.
In theory,
VDSL2 can achieve the highest transmission rates of 100 Mbit/s, and more perfectly
using the high-speed performance of short distance.
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Asynchronous transfer mode is a high-performance, cell-oriented switching and
multiplexing technology that utilizes fixed-length packets to carry different types of
traffic. ATM was originally conceived as a high-speed transfer technology for voice,
video, and data over public networks.