46
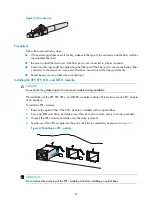
Connecting the switch to the network through the AUX port
You need an AUX cable when configuring a switch with the remote modem dial-up approach.
Introduction
An AUX cable is an 8-core shielded cable. At one end of the cable is an RJ-45 connector and at the other
end is a DB-9 (male) connector. Plug the RJ-45 connector into the AUX port of the switch and the DB-9
(male) connector into the DB-9 (female) port of the modem. An AUX cable is the same as a console cable.
For more information, see
Connection procedure
To connect the AUX port:
1.
Plug the RJ-45 connector of the AUX cable into the AUX port of the switch.
2.
Plug the DB-9 (male) connector at the other end into the serial port of the modem.
Connecting the switch to the network through a copper Ethernet
port
The 10/100/1000Base-T copper ports of the switch support MDI/MDI-X auto-sensing. They are
connected to the network through category-5 or above twisted pairs that are equipped with RJ-45
connectors.
NOTE:
No Ethernet twisted pair cables are shipped with the switch. Prepare them by yourself.
Connection procedure
To connect a 10/100/1000Base-T port:
1.
Plug one end of an Ethernet twisted pair cable into the copper Ethernet port (RJ-45 port) to be
connected on the switch.
2.
Plug the other end of the cable into the RJ-45 port of the peer device.
Connecting the switch to the network through a fiber Ethernet
port
Use an optical fiber to connect an XFP, SFP, CFP, SFP+, or QSFP+ port on the switch to the network. You
must install a transceiver module to the switch, and then insert the fiber connector to the module.
Introduction to fiber connector
Fiber connectors are indispensable passive components in an optical fiber communication system. They
allow the removable connection between optical channels, which makes the optical system debugging
and maintenance more convenient and the transit dispatching of the system more flexible. Among
various fiber connectors, only the LC connector is described here.