120
Adjustments for Competition
Rear Suspension Adjustments
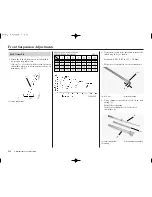
4. Calculate the race sag dimension.
To do this, subtract the loaded with rider
dimension (step 3) from the unloaded
dimension (step 2).
Standard Race Sag:
3.9 in (100 mm)
Adjust spring pre-load as necessary to obtain
the desired handling results.
Decreasing the race sag dimension (example:
3.5 in, 90 mm) improves turning ability for
tight terrain at the cost of slightly reduced
straight line stability.
Increasing the race sag dimension (example:
4.3 in, 110 mm) may improve stability on
faster terrain with less turns, but will reduce
turning performance slightly and may upset
the balance between the front and rear
suspension, producing a harsher ride. This
will happen if the adjustment shifts the
effective wheel travel toward the more
progressive end of its range.
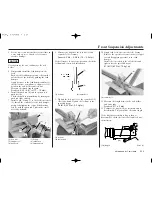
5. Measure the loaded without rider dimension.
Do this with your motorcycle set at the
standard race sag.
Rear Suspension Race Sag
Setting the proper race sag (ride height) is very
important for competition use.
Race sag refers to the amount of rear wheel
travel used by your motorcycle at rest, ready to
ride, with you on the seat. As a general rule of
thumb, the race sag dimension should be about
one-third of the maximum travel.
On your motorcycle, ride height is changed by
adjusting the rear suspension spring pre-load.
Spring Pre-load & Race Sag Adjustment
The following adjustment procedure establishes
the correct starting point for any suspension
tuning — the proper rear spring pre-load
adjustment for your specific needs.
Your motorcycle should be at normal racing
weight, including fuel and transmission oil. You
should be wearing all your normal protective
apparel. You will need two helpers.
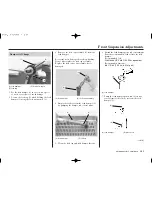
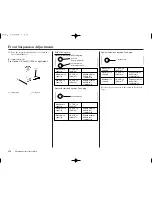
To calculate the proper adjustment, it is necessary
to measure between two fixed points — from the
center of the rear fender mounting bolt to the
center of the chain adjuster lock nut as illustrated
here — for three different situations:
unloaded: motorcycle on workstand with rear
suspension fully extended, no rider.
loaded with rider: motorcycle on ground, with
rider.
loaded without rider: motorcycle on ground,
without rider.
1. Support your motorcycle on a workstand with
the rear wheel off the ground.
2. Measure the unloaded dimension.
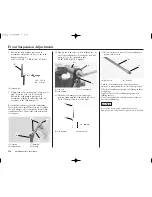
3. Measure the loaded with rider dimension.
Remove the workstand. With two helpers
available, sit as far forward as possible on
your motorcycle’s seat, wearing your riding
apparel.
Ask one helper to steady your motorcycle
perfectly upright so you can put both feet on
the pegs. Bounce your weight on the seat a
couple of times to help the suspension
overcome any situation and settle to a good
reference point.
Ask the other helper to measure the loaded
with rider dimension.
Example:
Unloaded
= 23.6 in (600 mm)
– Loaded
= 19.7 in (500 mm)
Race Sag
= 3.9 in (100 mm)
UNLOADED MEASUREMENT
(without rider)
EXAMPLE: 23.6 in (600 mm)
REAR FENDER MOUNTING BOLT
CHAIN ADJUSTER LOCK NUT
REAR FENDER MOUNTING BOLT
CHAIN ADJUSTER LOCK NUT
LOADED
(with rider)
EXAMPLE: 19.7 in (500 mm)
BIKE LOADED
(without rider)
EXAMPLE: 21.7 in (550 mm)
Example:
Unloaded
= 23.6 in (600 mm)
– Loaded
= 21.7 in (550 mm)
Sag
= 2.0 in (50 mm)
(Without Rider)
Summary of Contents for CRF250X 2006
Page 1: ...2006 Honda CRF250X OWNER S MANUAL COMPETITION HANDBOOK ...
Page 10: ...6 Motorcycle Safety ...
Page 16: ...12 Before Riding ...
Page 26: ...22 Basic Operating Instructions ...
Page 150: ...146 Taking Care of Unexpected ...
Page 165: ...Technical Information 161 Wiring Diagram ...
Page 166: ...162 Technical Information ...
Page 177: ...Memo 173 ...
Page 178: ...174 Memo ...
Page 179: ...Memo 175 ...