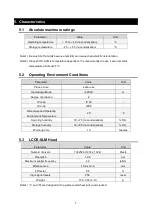
9
6.
Internal configuration
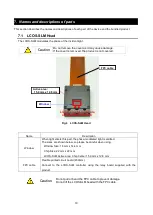
As shown in Fig. 2, the LCOS-SLM consists of a glass substrate, a transparent electrode, an alignment film,
a liquid crystal layer aligned in parallel, a dielectric multilayer mirror, and a silicon substrate. An active matrix
circuit is formed on the silicon substrate to apply voltage to the pixel electrode and the pixel electrode.
The number of pixels of the X15223 series is 1272
×
1024, and arbitrary control is possible for each pixel.
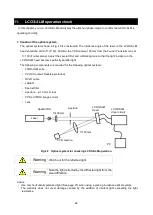
The display properties set on the PC are as shown in Fig. 3, and the input signals in the right eight columns
are ignored. Therefore, the signal of 1272
×
1024 pixels is displayed from the left.
Phase modulation is performed on the liquid crystal layer. The phase is modulated by the parallel aligned
liquid crystal layer, and the phase modulation amount changes according to the applied voltage. Although
liquid crystals generally respond non-linearly to input voltages, linear phase modulation is achieved with
respect to input values by incorporating a look-up table (LUT: Look-Up Table) within the drive circuit that
converts 8 bits of input into 12 bits.
Dielectric multilayer mirrors help to improve light utilization efficiency. The use of a dielectric multilayer
mirror makes it possible to achieve a light utilization efficiency of 90% or more in a specific wavelength range,
which is higher than that of LCOS-SLM composed of aluminum mirrors. The aluminum mirror type can be
used in a wider wavelength range than the type equipped with a dielectric multilayer mirror. However, the light
resistance is lower than that with a dielectric multilayer mirror, so be careful when using a high-power light
source.
Fig.2 Configuration of LCOS-SLM
Fig.3 Relationship between LCOS-SLM pixel structure and display properties
(Right 8 columns not used)
1272
1024
8
Glass substrate
Alignment films
Liquid crystal layer
Dielectric mirror
Silicon substrate
Transparent electrode