16
GUIDE TO DIGITAL RADIO
This unit enables you to receive and listen to DAB radio programmes. Digital Audio
Broadcast (DAB) uses digital signals rather than traditional analogue signals, the result of
which enables near CD-quality audio and virtually interference-free reception. DAB also
enables broadcasters to transmit additional data along with the audio including other audio
channels, text and in the future , perhaps computer data and images.
Digital radio is broadcast as groups of data called ensembles or multiplexes. Each
multiplex can contain a number of stations (services) and each station contains a primary
services and can contain secondary services.
Each multiplex is transmitted in a set
frequency range and received by the unit for
decoding. This unit enables
in frequency band III
(174-240 MHz) and store the services in each multiplex for you to access. The number of
multiplexes you receive will vary depending on your location. Band III is divided into 41
channels identified as 5A to 13F. Each channel can contain one multiplex . Channels
allocated to the UK Are in the range 11B to12D.
Multiplexes and stations have labels (names) which are used to identify them. Instead of
needing to know a particular frequency to listen to a favourite
Secondary services and additional data such as text
containing programme or multiplex information are also easily accessed using this unit.
the reception of multiplex broadcasts
station it is simply selected
via the station name in the station list.
DAB OPERATION
1. Press the DAB button to select DAB operation.
2. Search
by pressing the Auto Scan button.
3. The number of available stations will be shown in the LCD display.
for available DAB stations
DAB Operation (Continued)
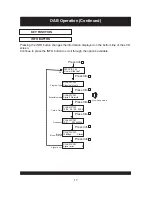
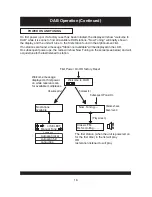
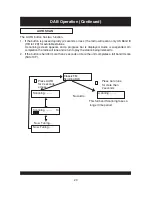
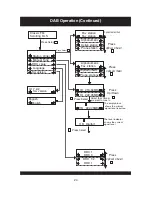
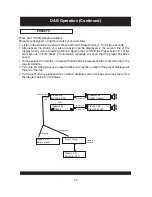
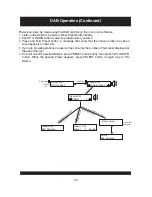
USER INTERFACE
This section details all the menus and structured sub menus the user can access via the
interface.
Each illustration shows the symbols, text and format of each menu displayed, reflecting what
may be displayed on the LCD. The LCD defines the character set shown and therefore this is
only an example of the text displayed.
GENERAL BEHAVIOUR
When navigating through menus, any list will cycle to the beginning once all the menus
have been scrolled through.
If a button has no specific function in a menu or mode then pressing it will exit the menu or
mode currently selected.