141
8.3 Remote Monitoring with E-Map
You can use the Remote E-Map to monitor the video and I/O devices connected to the GV-IP
Speed Dome.
Creating an E-Map for the GV-IP Speed Dome
With the E-Map Editor, you can create an E-Map for the GV-IP Speed Dome and I/O devices
connected to the dome. The E-Map Editor is available in two applications: Main System and
E-Map Server. The following is an example of running the E-Map Editor included in the Main
System.
1. In the Windows
Start
menu, go to
Programs
, select
GV folder
and click
E-Map Editor
.
2. To create an E-Map, click the
Add Map
button on the toolbar. A New Map file appears.
3. Double-click the New Map file, and click the
Load Map
button on the toolbar to import a
graphic file.
4. To create a host, click the
Add Host
button on the toolbar and select
Add Video Server
.
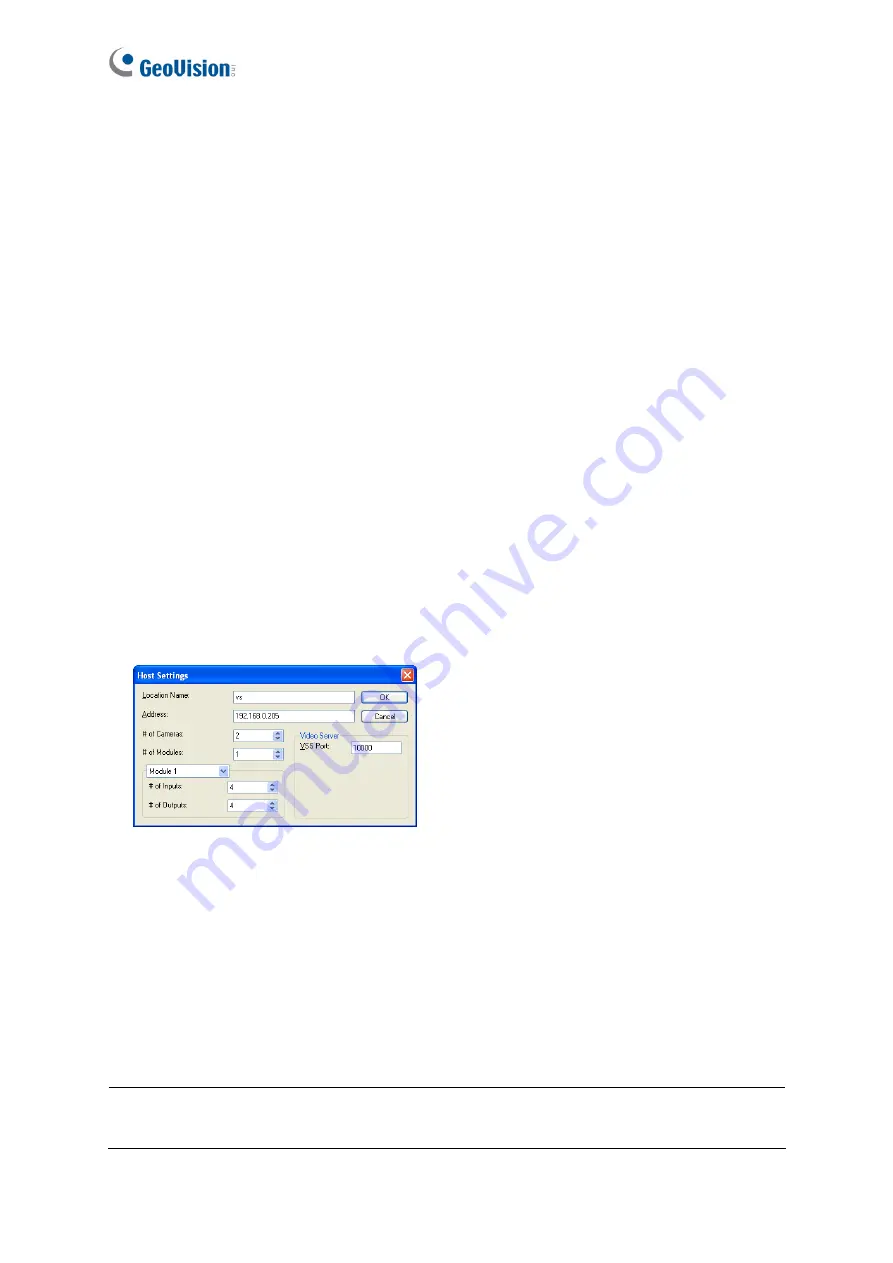
5. Right-click the created New Host in the Host View, and select
Host Settings
.
This dialog
box appears.
Figure 8-11
6. Give the GV-IP Speed Dome a location name, and type its IP address (or domain name).
Modify the default VSS port
10000
if necessary to match that of the GV-IP Speed Dome.
7. Click
OK
to save the settings.
8. Expand the created host folder. Drag and drop the icons of cameras and I/O devices onto
the imported E-Map.
9. Close the E-Map Editor. Click
Yes
when you are prompted to save the file.
Note:
For details on creating an E-Map file on the E-Map Server, see “E-Map Application”
in
GV-DVR/NVR User’s Manual
or
GV-VMS User’s Manual
.

























