489 GENERATOR MANAGEMENT RELAY – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
11
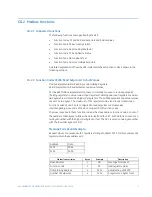
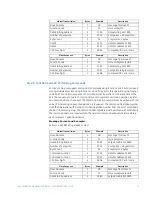
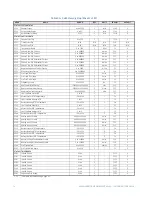
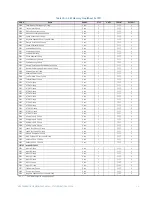
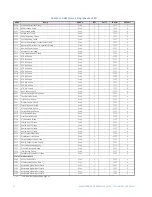
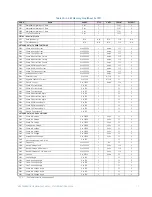
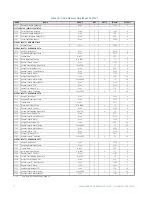
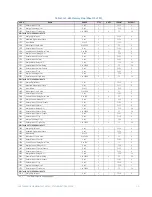
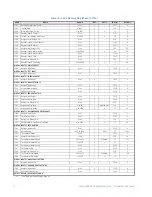
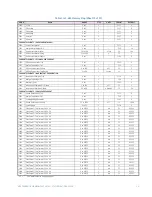
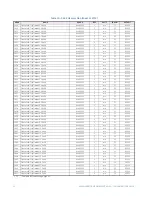
CG.3 Modbus Memory Map
CG.3.1 Memory Map Information
The data stored in the 489 is grouped as Setpoints and Actual Values. Setpoints can be
read and written by a master computer. Actual Values are read only. All Setpoints and
Actual Values are stored as two byte values. That is, each register address is the address of
a two-byte value. Addresses are listed in hexadecimal. Data values (Setpoint ranges,
increments, and factory values) are in decimal.
N
Note
Many Modbus communications drivers add 40001d to the actual address of the register
addresses. For example: if address 0h was to be read, 40001d would be the address
required by the Modbus communications driver; if address 320h (800d) was to be read,
40801d would be the address required by the Modbus communications driver.
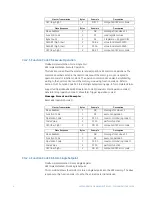
CG.3.2 User-Definable Memory Map Area
The 489 contains a User Definable area in the memory map. This area allows remapping of
the addresses of all Actual Values and Setpoints registers. The User Definable area has two
sections:
1. A Register Index area (memory map addresses 0180h to 01FCh) that contains
125 Actual Values or Setpoints register addresses.
2. A Register area (memory map addresses 0100h to 017Ch) that contains the
data at the addresses in the Register Index.
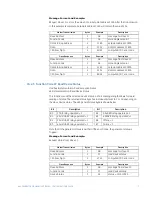
Register data that is separated in the rest of the memory map may be remapped to
adjacent register addresses in the User Definable Registers area. This is accomplished by
writing to register addresses in the User Definable Register Index area. This allows for
improved throughput of data and can eliminate the need for multiple read command
sequences.
For example, if the values of Average Phase Current (register addresses 0412h and 0413h)
and Hottest Stator RTD Temperature (register address 04A1h) are required to be read from
an 489, their addresses may be remapped as follows:
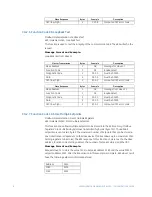
1. Write 0412h to address 0180h (User Definable Register Index 0000) using func-
tion code 06 or 16.
2. Write 0413h to address 0181h (User Definable Register Index 0001) using func-
tion code 06 or 16.
(Average Phase Current is a double register number)
3. Write 04A1h to address 0182h (User Definable Register Index 0002) using func-
tion code 06 or 16.
A read (function code 03 or 04) of registers 0100h (User Definable Register 0000) and
0101h (User Definable Register 0001) will return the Average Phase Current and register
0102h (User Definable Register 0002) will return the Hottest Stator RTD Temperature.