10
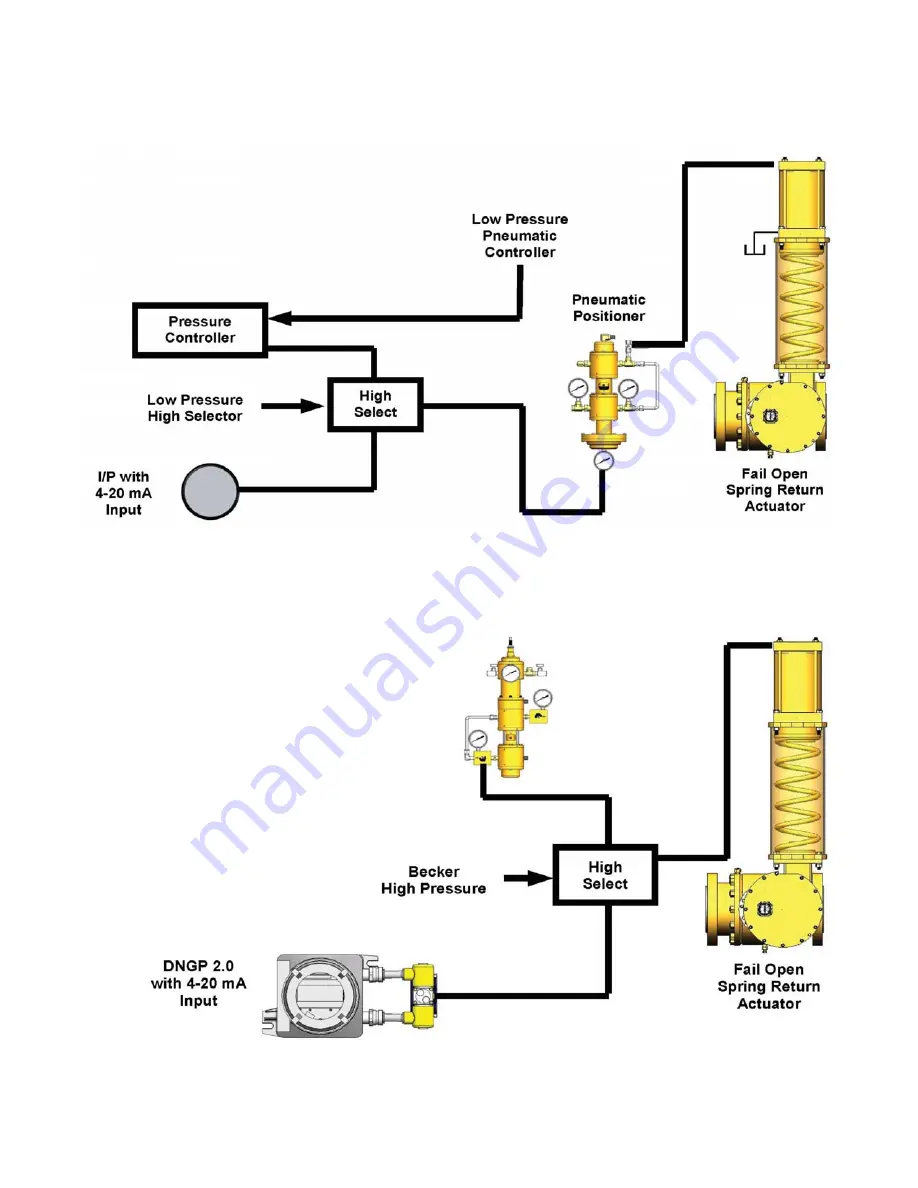
Electro-Pneumatic Positioner Pressure
Control Override*
Conventional fl ow control with PCO (Pressure Control
Override) is accomplished by sending a signal to the
positioner from an I/P transducer or pneumatic controller.
A HIGH SELECT RELAY determines if the positioner is
controlled by the pneumatic controller (pressure control)
or the I/P (fl ow control).
Figure 10 -
Conventional Flow Control with Pressure Control Override (PCO)
By exchanging the I/P with an electro-pneumatic
positioner, the pneumatic positioner can be eliminated.
Using the DNGP for the electro-pneumatic positioner
allows the unit to fail open, closed, or in last position on
loss of 4-20 mA signal. Becker high pressure VRP pilots
and Becker high pressure HIGH/LOW selector relays
ideally complement the DNGP electro-pneumatic
positioner for high or low pressure override.
*For double acting systems, Becker double acting pilots are used. See the sampling
of pneumatic schematics for specific pressure control override applications on the
next two pages.
Figure 11 -
Flow Control with Electro-Pneumatic Positioner and PCOH High Pressure Override
Signal Selector











































