154
- Before Using the Optional Wireless LAN
•
Microwave ovens may interfere with the operation of WLAN devices since they operate in the same 2.4 GHz
frequency range as IEEE802.11b/g/n devices. Interference by microwaves does not occur with IEEE802.11a
radio which operates in the 5 GHz RF band.
•
Wireless devices that transmit in the 2.4 GHz range may interfere with operation of WLAN devices in
IEEE802.11b/g/n modes. Symptoms of interference include reduced throughput, intermittent disconnects, and
many frame errors. It is HIGHLY recommended that these interfering devices be powered off to ensure proper
operation of the WLAN device.
Deactivating/Disconnecting the WLAN Device
Disconnecting the WLAN device may be desired in certain circumstances (to extend battery life) or where certain
environments require it (i.e. hospitals, clinics, airplanes, etc.). The WLAN device can be deactivated by using the
Wireless On/Off Switch, and it can be disconnected in Windows using the WLAN icon in the system tray (Note that
disconnecting via the icon in the system tray does not turn off the radio; it continues to transmit and receive even
though it’s not connected.).
Disconnection Using the Icon in the Taskbar
Note that disconnecting via the icon in the system tray does not turn off the radio; it continues to transmit and receive
even though it’s not connected.
1
Right-click the WLAN icon in the taskbar at the bottom right of your screen.
2
Choose
Disconnect from a network
.
Deactivation Using the
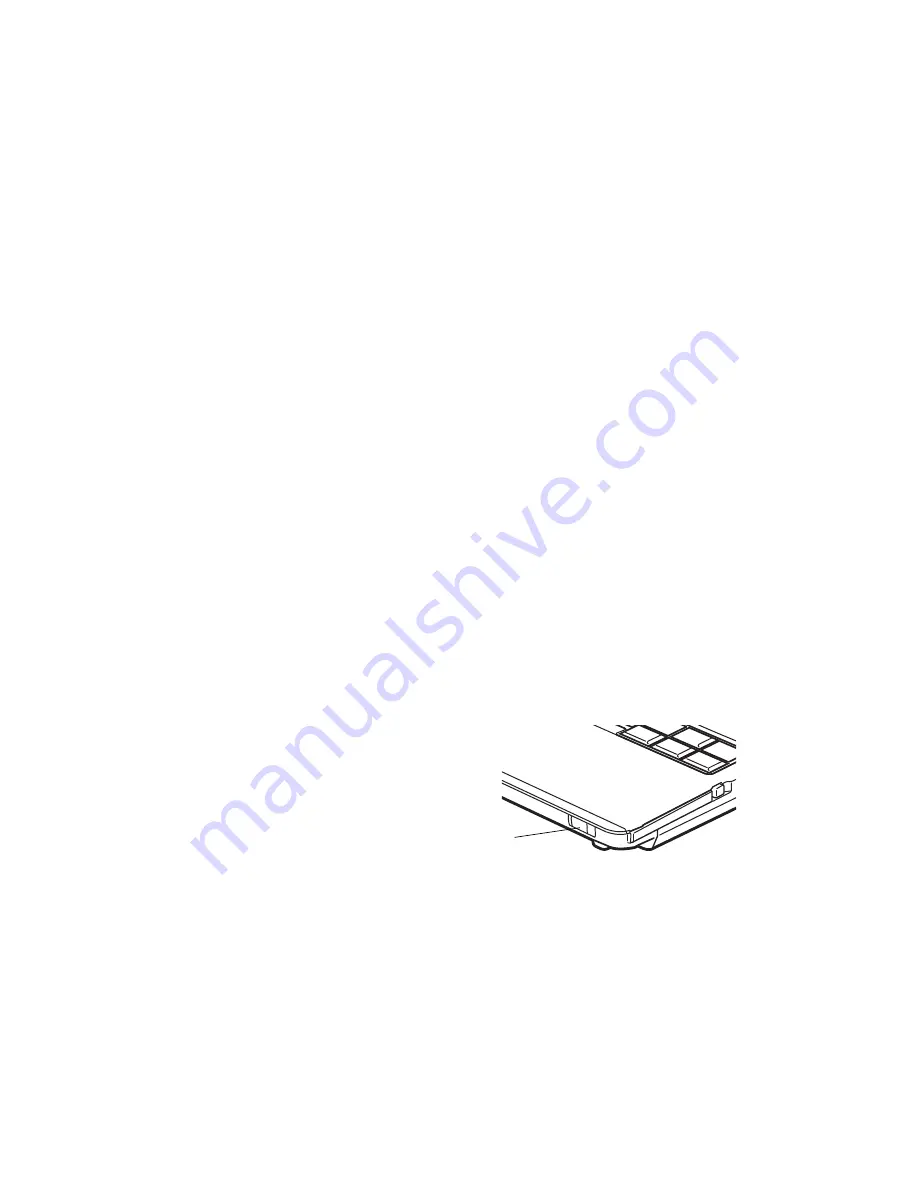
Wireless On/Off Switch
The WLAN device can be deactivated quickly
and efficiently by toggling the Wireless On/Off
Switch to the Off position.
The Wireless On/Off
switch has no effect on non-Wireless LAN
models.
Figure 47. Wireless LAN On/Off Switch Location
Wireless
Device
Switch
















































