4-2
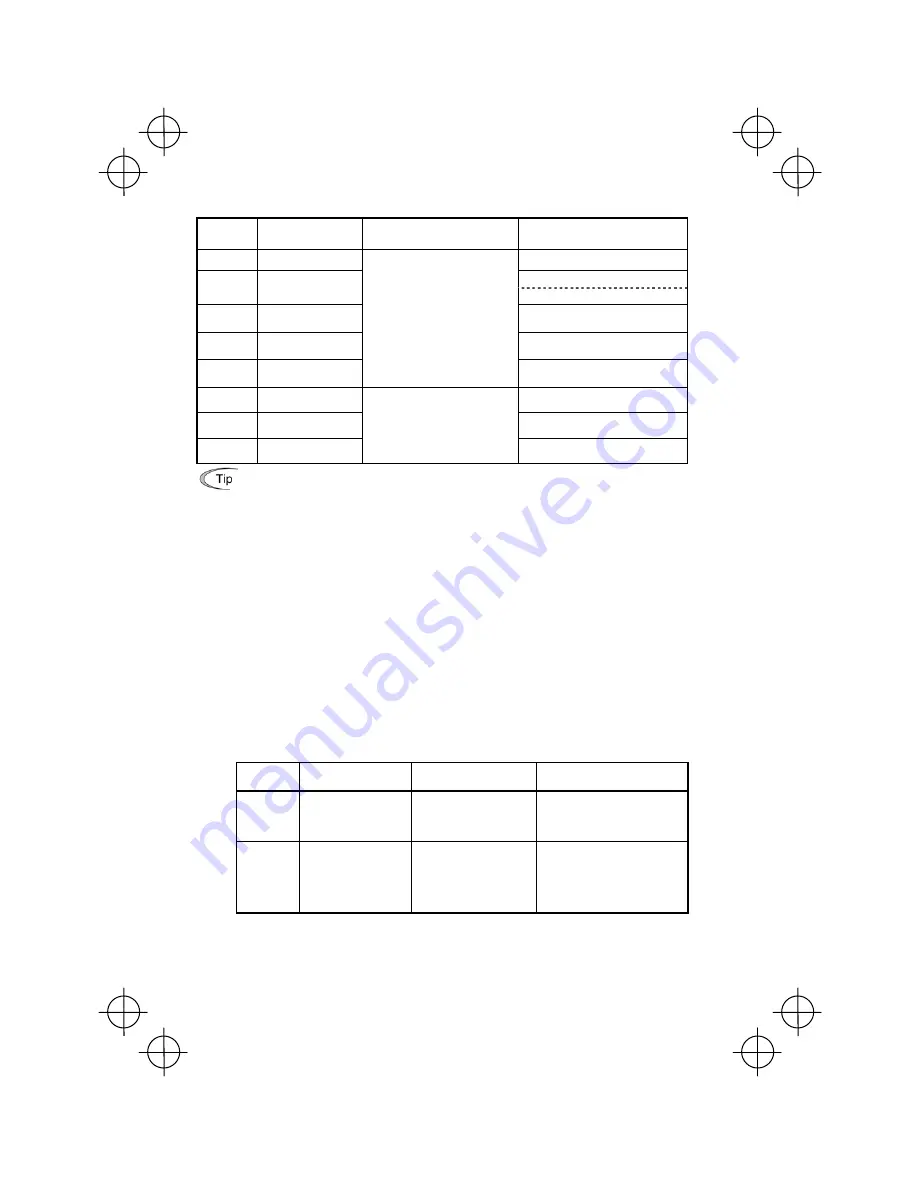
Table 4.1 Settings of Function Code Data before Driving the Motor for a Test
Function code
Name
Function code data
Factory setting
f 04
Base frequency
60.0 (Hz)
230 (V)
f 05
Rated voltage
(at base frequency)
460 (V)
p 02
Motor parameter
(Rated capacity)
Applicable motor rated capacity
p 03
Motor parameter
(Rated current)
Rated current of applicable motor
p 99
Motor Selection
Motor ratings (printed on the
nameplate of the motor)
0: Characteristic of motor, 0 (Fuji
standard 8-series motors)
f 03
Maximum frequency
60.0 (Hz)
f 07
Acceleration time 1*
20.0 (s)
f 08
Deceleration time 1*
System design values
* For a test-driving of the motor,
increase values so that they are
longer than your system design
values. If the set time is short, the
inverter may not start running the
motor.
20.0 (s)
In any of the following cases, the default settings may not produce the best results for auto torque boost,
torque calculation monitoring, or auto energy saving, since the standard settings of motor parameters for
Fuji motors are not applicable. Tune the motor parameters according to the procedure set forth below.
• The motor to be driven is not a Fuji product or is a non-standard product.
• The cabling between the motor and the inverter is long.
• A reactor is inserted between the motor and the inverter.
<
Tuning procedure
>
1) Preparation
Referring to the rating plate on the motor, set the following function codes to their nominal ratings:
• F04: Base frequency
• F05: Rated voltage (at Base frequency)
• P02:
Rated
capacity
• P03:
Rated
current
2) Selection of Tuning Process
Check the situation of the machine system and choose between "Tuning while the motor is stopped (P04
= 1)" and "Tuning while the motor is running (P04 = 2)." In the case of "Tuning while the motor is running
(P04 = 2)," also adjust the acceleration and deceleration times (F07 and F08) and set the rotation
direction properly so that it matches the actual rotation direction of the machine system.
Data for
P04
Motor parameters
subject to Tuning:
Action
Choose the process when:
1
Primary resistance (%R1)
Leakage reactance (%X)
Measure %R1 and %X while
the motor is stopped.
The motor cannot be rotated, or
more than 50% of the rated load
would be applied on the motor if
rotated.
2
Primary resistance (%R1)
Leakage reactance (%X)
No-load current
Measure %R1 and %X while
the motor is stopped, and
later no-load current while
the motor is running. (At
50% of the Base frequency).
Even if the motor is rotated, it is
safe and the load applied on the
motor would be no more than 50%
of the rating. (If you do the tuning
with no load, you will get the
highest precision.)
Upon completion of the tuning, the primary resistance %R1 will be automatically saved into P07, the
leakage reactance %X into P08, and the no-load current into P06.
Summary of Contents for FRENIC-ECO
Page 111: ...5 3 F codes Fundamental Functions The shaded function codes are applicable to the quick setup...
Page 114: ...5 6 F code continued...
Page 115: ...5 7 E codes Extension Terminal Functions...
Page 116: ...5 8 E code continued...
Page 119: ...5 11 E code continued...
Page 121: ...5 13 P codes Motor Parameters The shaded function codes are applicable to the quick setup...
Page 122: ...5 14 H codes High Performance Functions...
Page 123: ...5 15 H code continued...
Page 126: ...5 18 J code continued...
Page 127: ...5 19 J code continued...
Page 128: ...5 20 y codes Link Functions...
Page 129: ...5 21 y code continued...
Page 141: ...5 33 Example of Operating Characteristics...
Page 217: ...8 6 8 3 Common Specifications...
Page 218: ...8 7...
Page 223: ...8 12 8 5 External Dimensions 8 5 1 Standard models Unit inch mm 10 2 260...
Page 227: ...8 16 8 5 3 Multi function Keypad Unit inch mm...
Page 246: ...Fuji Electric FA Components Systems Co Ltd Fuji Electric Corp of America 2007 11 K07 K07 10CM...
















































