ExRobotics B.V.
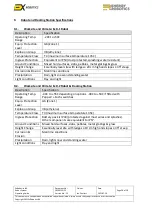
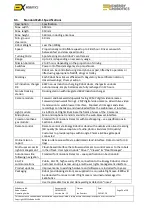
Robot System
Operating Guide
Document No.:
20190122IP1
Version No.: 12
Owner:
Ian Peerless
Date:
2021-07-20
Page 14 of 30
This document is considered an uncontrolled copy when printed. Always ensure that you print and use a current version.
Copyright 2021 ExRobotics B.V.
6.
Autonomous Missions
6.1.
Overview
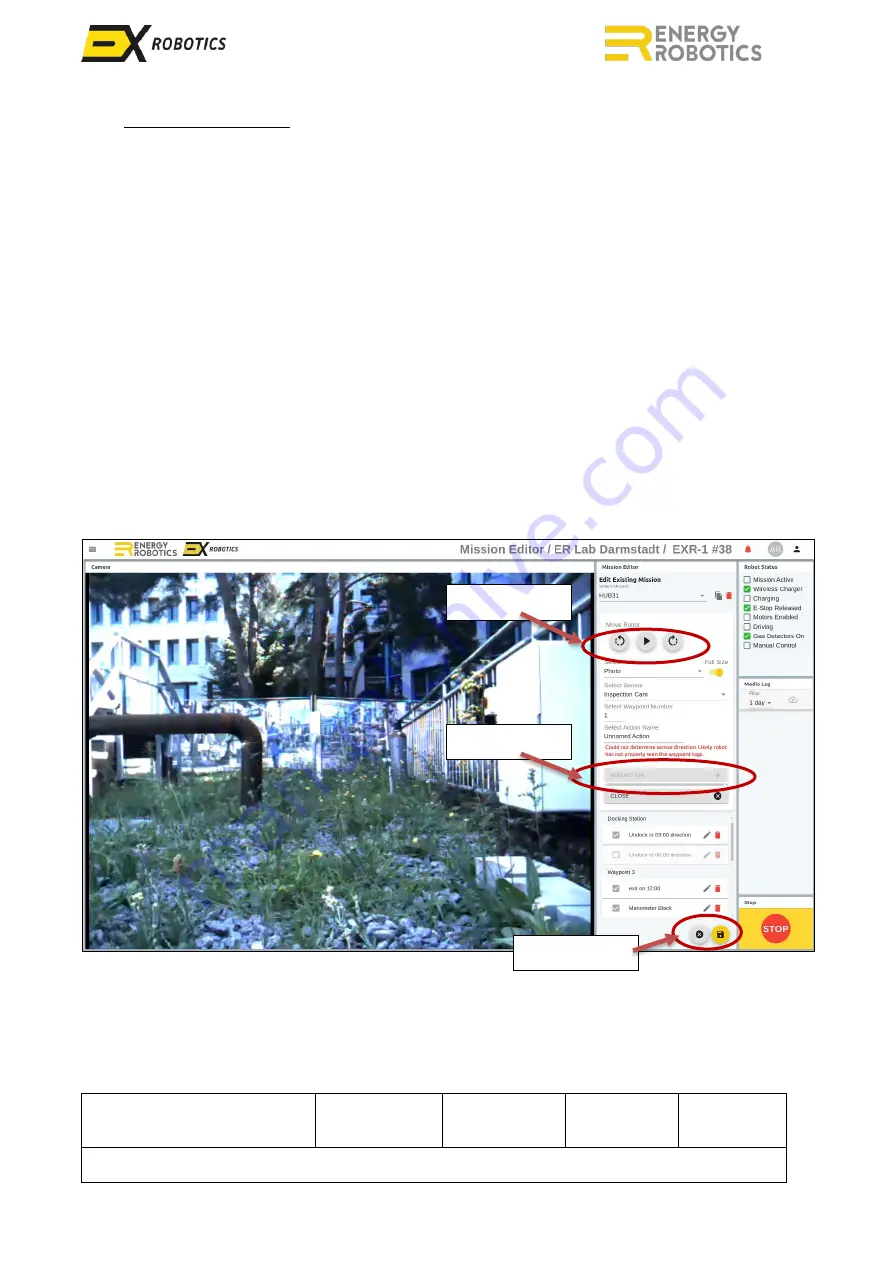
A robot mission is typically a circuit that starts and finishes at a docking station. During the circuit
the robot will perform actions for points of interest when the robot is located at a waypoint:
▪
A typical action is to record a video, snapshot, sound, or sensor reading.
▪
Actions are targeted at points of interest (POIs). This is a 3D location at which the appropriate
camera or sensor is targeted. Examples of POIs are valves, flanges and pumps. To target the
POI the robot will usually need to change its azimuth (rotate) and in some cases will require a
camera to lift its field of view (elevate). There can be more than one action at a POI.
▪
Waypoints are 2D locations from which POIs are observed. There can be multiple POIs at a
waypoint. In Line-following navigation, waypoints are defined by an array of chili-tags.
▪
There can be multiple waypoints on a mission.
Robots perform their missions using orange lines on the ground (line following navigation), chili-
tags (tag based inspections) and/or a virtual model created by
the a robot’s LiDAR module (full 3D
navigation). The deployment guide describes how to establish the required infrastructure. This
manual describes how to use that infrastructure using this mission editor screen.
Robot control
Add Action
Save Mission