RTC - 8564 JE/NB
Page - 5
MQ - 322 - 04
8. How to use
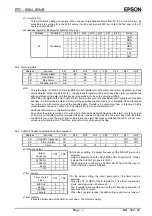
8.1. Register table
Address
Function
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
00
Control
1
TEST 0 STOP 0 TEST 0
0
0
01 Control
2
0
×
0
TI / TP
AF
TF
AIE
TIE
02
Seconds
VL 40 20 10 8 4 2 1
03 Minutes
×
40 20 10 8 4 2 1
04 Hours
×
×
20 10 8 4 2 1
05 Days
×
×
20 10 8 4 2 1
06 Weekdays
×
×
×
×
×
4 2 1
07
Months / Century
C
×
×
10 8 4 2 1
08
Years
80 40 20 10 8 4 2 1
09
Minute
Alarm
AE 40 20 10 8 4 2 1
0A Hour
Alarm
AE
×
20 10 8 4 2 1
0B Day
Alarm
AE
×
20 10 8 4 2 1
0C Weekday
Alarm
AE
×
×
×
×
4 2 1
0D CLKOUT
frequency
FE
×
×
×
×
×
FD1
FD0
0E Timer
control
TE
×
×
×
×
×
TD1
TD0
0F
Timer
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
Notes ;
(1) When the power is turned on initially, the FD1 and FD0 bits are cleared to 0. Also, FE and VL bits are set to 1, but
because other the register values of other bits are unknown, always make their initial settings. When doing so,
do not make settings for date and time that are impossible. We do not guarantee proper operation of the clock
for such settings.
(2) While there is a bit at address 00 for setting the test mode, the test mode is a special operation mode that is used
by EPSON for testing devices. Be sure not to set it to 1. If it is set to the test mode, all operations of the device will
not be guaranteed. Therefore, be careful when access to address 00.
(3) Be sure to set bit '0' of address 00,01 (Control1,2) to zero.
(4) All count data at address 02 through 05 and 08 through 0B is in the BCD format.
(5) Write to bit '
×
' is not possible, and its read-out value is not fixed. Be sure to mask it after bit '
×
' is read out.
8.2. Register description
8.2.1. Control register 1
Address
Function
bit 7
bit 6
bit 5
bit 4
bit 3
bit 2
bit 1
bit 0
00 Control
1
TEST 0 STOP 0 TEST 0
0
0
•
TEST
The two TEST bits are for testing devices. Therefore be sure to set them to zeros. If they are accidentally set
to 1, they may immediately modify the clock data or result in abnormal time.
•
STOP
When this bit becomes zero, the device's time function operates. When it is set to 1, all internal count down
chain are goes into the zero clear state. If it is cleared together with the time reporting, the time can be
adjusted accurately up to one second. As for output of CLKOUT,
STOP doesn't affect frequency output of 32768 Hz.But output stops at the time of frequency setting except
32768 Hz by STOP =1.