IDSOFT IFU (Iss 09/15)
Page 4
Seat Belt:
A lap belt is to restrain the wheelchair occupant during
normal use. The wheelchair is suitable for use as a seat
in the motor vehicle, however the lap belt should not
be used. Please refer to the section of using the
wheelchair as a seat in a motor vehicle.
The lap belt should be adjusted to suit each user. The
length of the belt can be adjusted by the tri-glides (as
shown in the diagram overleaf). The lap belt has a
luggage-style large locking clip to fasten and unfasten
the lap belt. To fasten the lap belt, push the clip in to
the receiver until it locks in the position (which can be
heard by an audible click).
When fastened, the lap belt should be tight around the
user’s pelvis without causing discomfort or undue
pressure. This will help keep the user’s hips and pelvis
towards the back of the wheelchair. Use the tri-glides
(shown) to adjust the length of the lap belt. The length
of the lap belt should be checked each time the belt is
used.
There is a risk of suffocation from users ‘submarining’
(where they slide down the chair until the lap belt is
around the neck area). To reduce the risk of this, ensure
that the lap belt is used under supervision and is used
as instructed.
The lap belt may not be suitable for all users of
wheelchairs. Seek advice from your healthcare
professional before using the lap belt.
For Maximum Stability
The wheelchair is designed to be stable during normal
daily activities, provided that the user’s centre of gravity
is not moved outside of the footprint of the frame.
When propelling the wheelchair, the backrest should be
upright and it is recommended that user supports
should as posture belts are used.
Using the Wheelchair on a Gradient
Lean forward when self propelling up a gradient.
When self propelling down a gradient, the user should
keep their hands on handrim to control speed lean
backwards.
Be aware that the configuration of the wheelchair or
the condition of the gradient’s surface can adversely
affect the wheelchair’s stability.
!
Never go up or down a gradient diagonally.
Never exceed the maximum angle for
stability and use anti-tip wheels.
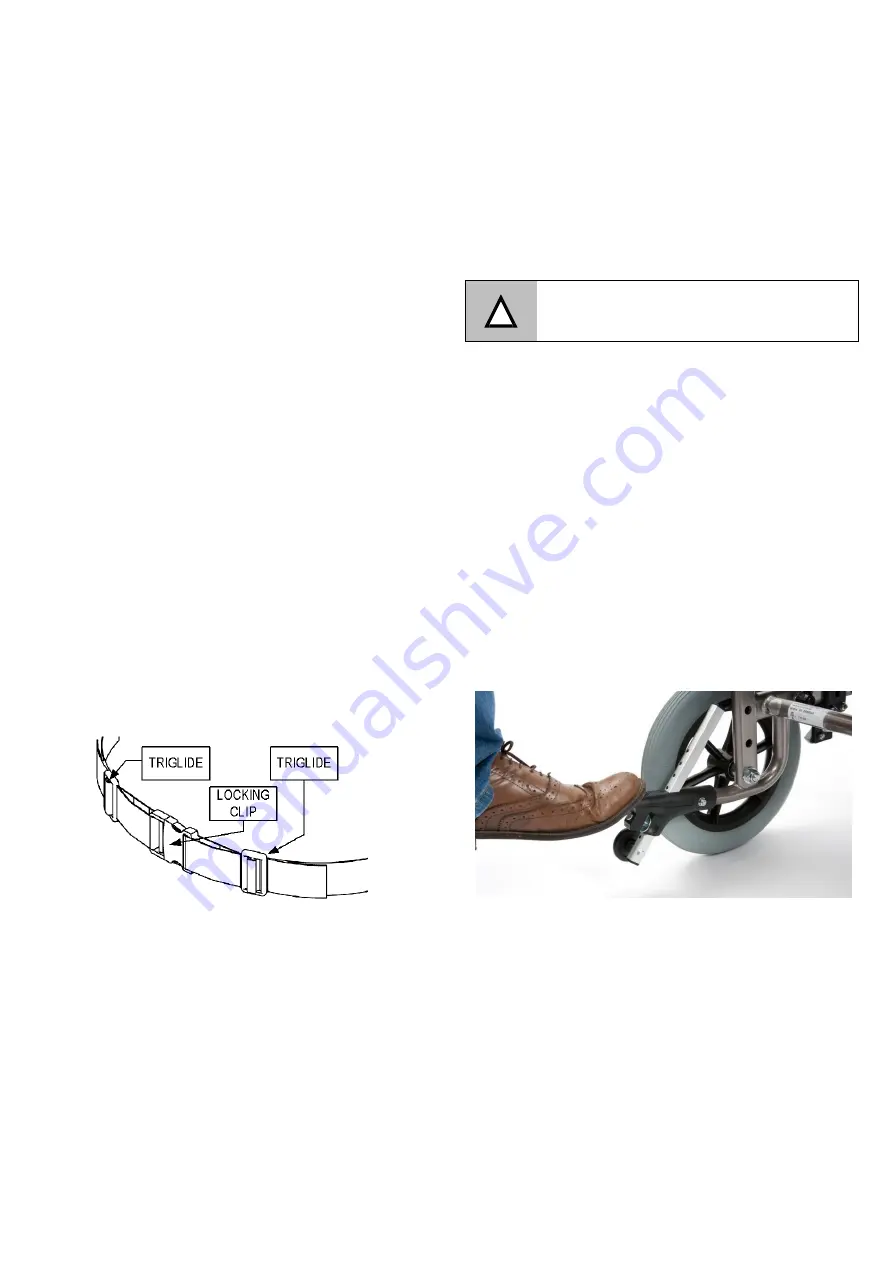
Negotiating a Kerb or Obstacle with the Wheelchair
An attendant can use the stepper tube to raise the front
castors (when mounting a kerb for example). To use,
push down on the stepper tube with a foot. Do not raise
the front castors by pushing down on the push handles
as this could result in damage to the wheelchair.
To mount a kerb
. Approach the kerb head on. Then the
attendant uses the stepper tube to raise the front
castors (as shown below), and lowers the front castors
on the raised kerb. Finally the attendant should push the
wheelchair forward, lifting it up slightly to mount the
kerb if required.
To go down a kerb
. Line up the front castors with the
edge of the kerb. The attendant uses the stepper tube to
raise the front castors and tip the user slightly back.
Keeping the castors raised, slowly lower the wheelchair
down the kerb.
Transferring
The user can laterally transfer without any aid, provided
he/she has the necessary muscular strength.
Please contact your healthcare professional for
instruction on how to do this.




























