TROUBLESHOOTING
8
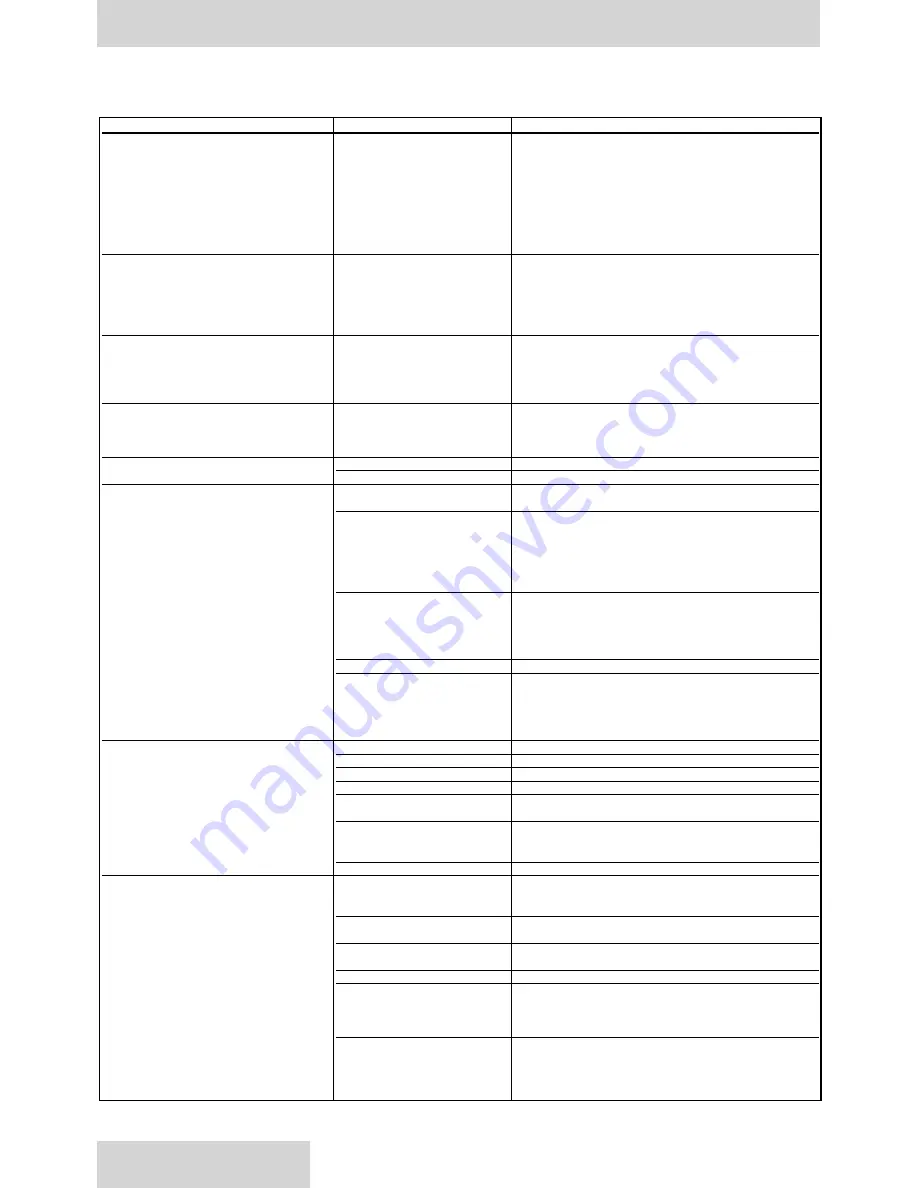
Component problems and circuit problems are often interrelated. An improper circuit may operate with apparent success but will
cause failure of a particular component within it. The component failure is the effect, not the cause of the problem. This general
guide is offered to help in locating and eliminating the cause of problems by studying their effects.
Effect of Trouble
Possible Cause
Fault Which Needs Remedy
pump
noisy
air in system
leak in suction line.
low fluid level.
turbulent fluid.
return lines above fluid level.
gas leak from accumulator.
excessive pressure drop in the inlet line from a
pressurized reservoir.
suction line strainer acting as air trap.
cavitation in rotating group.
fluid too cold, too viscous, or too heavy.
shaft speed too high.
suction line strainer too small, or strainer too dirty.
operating altitude too high.
boost pressure too low.
inlet flow too small for dynamic conditions.
misaligned shaft.
faulty installation.
distortion in mounting.
axial interference.
faulty coupling.
excessive overhung loads.
mechanical fault in pump.
piston and shoe looseness or failure.
bearing failure.
incorrect port plate selection or index.
eroded or worn parts in the displacement control.
erosion on barrel ports and port plate.
air in fluid.
see noisy pump above.
cavitation.
see noisy pump above.
high wear in pump.
excessive loads.
reduce pressure settings.
reduce speeds.
contaminant particles in fluid.
improper filter maintenance.
filters too coarse.
introduction of dirty fluid to system.
reservoir openings.
improper reservoir breather.
improper line replacement.
Improper fluid.
fluid too thin or thick for operating temperature range.
breakdown of fluid with time/temperature/shearing
effects.
incorrect additives in new fluid.
destruction of additive effectiveness with chemical aging
improper repair.
incorrect parts, procedures, dimensions, finishes.
unwanted water in fluid.
condensation.
faulty breather/strainer.
heat exchanger leakage.
faulty clean-up practice.
water in makeup fluid.
pressure shocks.
cogging load.
mechanical considerations.
worn relief valve.
needed repairs.
worn compensator.
needed repairs.
slow response in check valves.
replace or relocate.
excessive decompression
improve decompression control.
energy rates.
excessive line capacitance.
reduce line size or lengths.
(line volume, line stretch,
eliminate hose.
accumulator effects).
barrel blow-off.
re-check pump holddown,rotating group, drain pressure.
heating of fluid.
excessive pump leakage.
recheck case drain flow and repair as required.
fluid too thin.
improper assembly, port timing.
relief valve.
set too low (compared to load or to compensator).
instability caused by back pressure, worn parts.
compensator.
set too high (compared to relief).
worn parts.
pump too large for fluid needs.
select smaller pump displacement.
heat exchanger.
water turned off, too hot or too little flow.
fan clogged or restricted.
efficiency reduced by mud or scale deposits.
intermittent hydraulic fluid flow.
reservoir.
too little fluid.
improper baffles.
insulating air blanket that prevents heat rejection.
heat pickup from adjacent equipment.
.
www.comoso.com
Summary of Contents for P07 C-mod
Page 54: ...PQ HIGH RESPONSE CONTROL 54 PQ CONTROL IN PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT www comoso com ...
Page 55: ...PQ HIGH RESPONSE CONTROL 55 PQ CONTROL IN PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT www comoso com ...
Page 56: ...PQ HIGH RESPONSE CONTROL 56 PQ CONTROL IN PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT www comoso com ...
Page 57: ...PQ HIGH RESPONSE CONTROL 57 PQ CONTROL IN PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT www comoso com ...
Page 74: ...74 TEST PROCEDURE PQ CONTROL IN PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT www comoso com ...























