9. Modbus communication protocol
9.1 About the Modbus communication protocol
SGC 120/121 supports a custom protocol based on the standard Modbus over an RS-485 layer. operates in a slave mode and
responds to commands received from an external Modbus master.
9.2 Modbus connection details
The transmission mode used by SGC 120/121 is Modbus RTU (not Modbus ASCII). The byte format for communication is 1 start bit,
8 data bits, no parity bits and 1 stop bit, Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC).
Precautions
•
Find the slave ID from the SMPS and configure the same ID in the controller.
•
Enable the controller in the configuration of the SMPS after hardware connections are made.
•
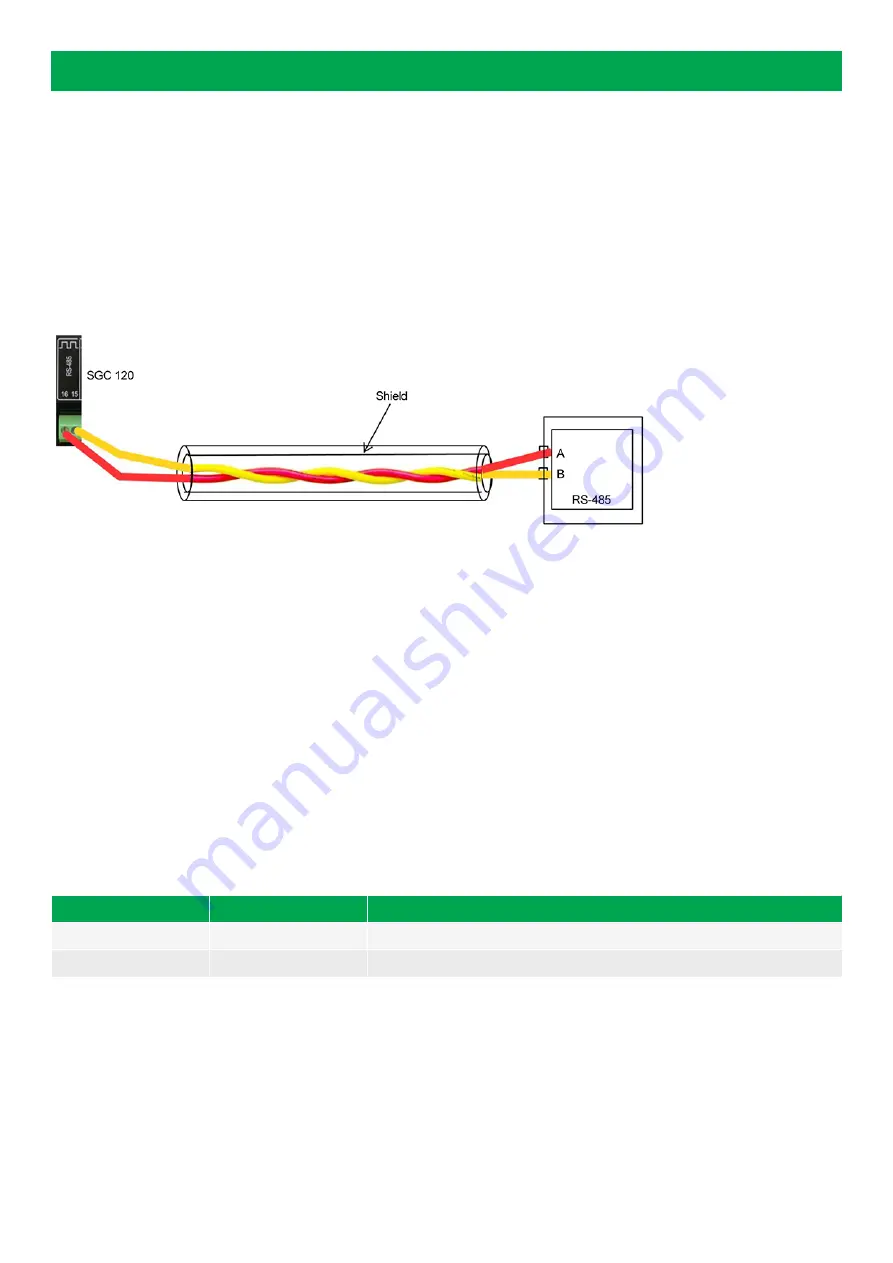
Connect the controller terminals 16 and 15 to the SMPS terminals A and B.
•
Use a two-core shielded cable for connection.
•
Use different colour wires for terminals 16 and 15 for easy detection and connection.
•
Route the wires properly ensuring they do not get short with any other wires.
•
Do not use multi strand wires for the connection.
9.3 Modbus functions
This genset controller operates as a Modbus slave that responds to certain commands (or functions, as defined by Modbus
standard) received from the Modbus master in appropriate format. Supported functions and respective command-response structure
is as shown below. If the command received from the Modbus master is other than the three functions mentioned below, an
exception message is generated.
Function code
Modbus name
Description
03
Read holding register
Reads one or more 16-bit registers from the slave device read/write location.
16
Write holding register
Writes one or more 16-bit registers to the slave device.
USER MANUAL 4189341226A UK
Page 47 of 72






























