ETR warning 4 (ETR WARNING 4)
[9]
ETR trip 4 (ETR TRIP 4)
[10]
Function:
The frequency converter can monitor the motor temperature in two dif-
ferent ways:
-
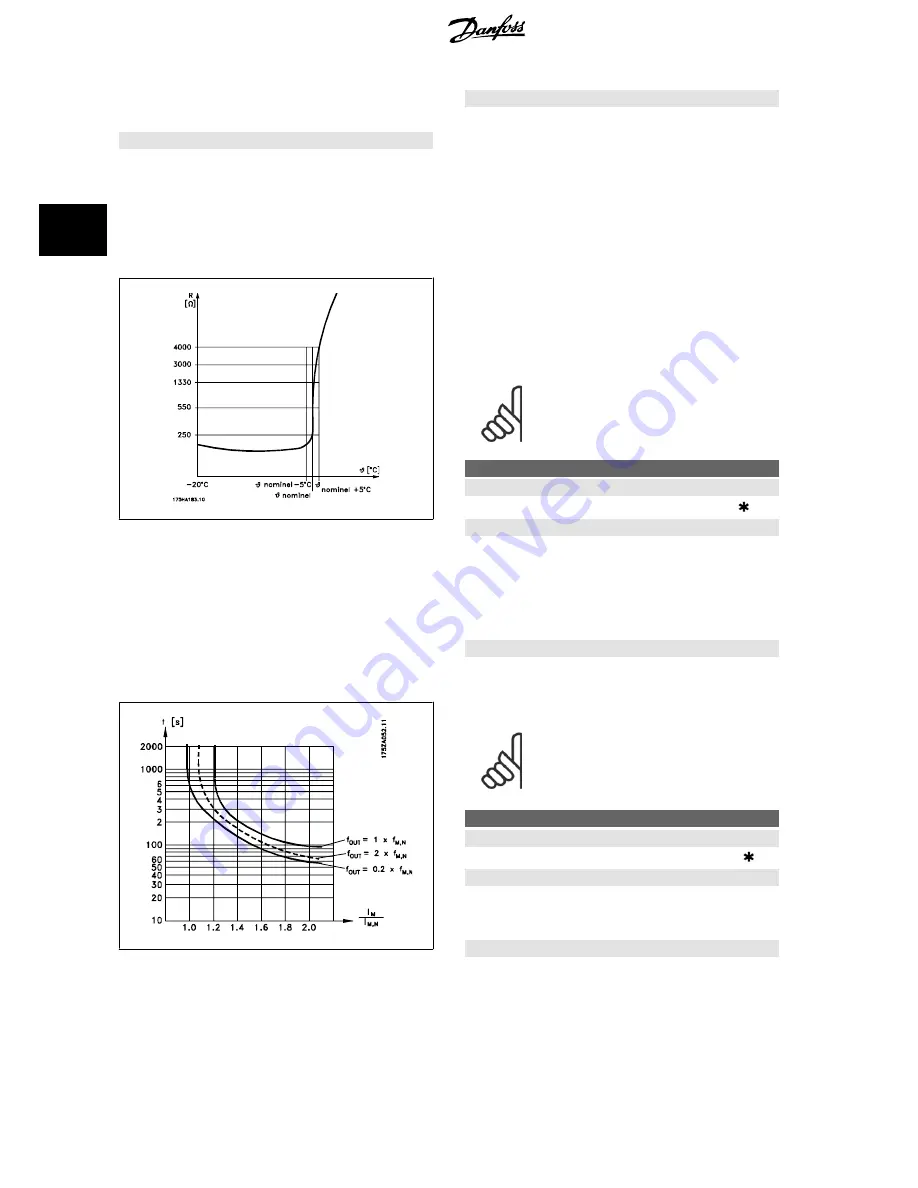
Via a PTC thermistor that is mounted on the motor. The ther-
mistor is connected between terminal 31a / 31b.
Thermistor
is
to be selected if a possibly integrated thermistor in the motor is
to be able to stop the frequency converter if the motor over-
heats. The cut-out value is 3 k
Ω
.
If a motor features a Klixon thermal switch instead, this can also
be connected to the input. If motors operate in parallel, the
thermistors/thermal switches can be connected in series (total
resistance lower than 3 k
Ω
).
-
Thermal load calculation (ETR - Electronic Thermal Relay),
based on present load and time. This is compared with the rated
motor current I
M,N
and rated motor frequency f
M,N
. The calcu-
lations take into account the need for lower loading at low
speeds due to the motor's internal ventilation being reduced.
ETR functions 1-4 correspond to Setup 1-4. ETR functions 1-4 do not
begin to calculate the load until you switch to the Setup in which they
have been selected. This means that you can use the ETR function even
when changing between two or more motors.
Description of choice:
Select
No protection
[0] if you do not want a warning or trip when a motor
is overloaded.
Select
Thermistor warning
[1] if you want a warning when the connected
becomes too hot.
Select
Thermistor trip
[2] if you want a trip when the connected ther-
mistor becomes too hot.
Select
ETR warning
if you want a warning when the motor is overloaded
according to the calculations. You can also programme the frequency
converter to give a warning signal via the digital output.
Select
ETR Trip
if you want a trip when the motor is overloaded according
to the calculations.
Select
ETR warning 1-4
if you want a warning when the motor is over-
loaded according to the calculations. You can also programme the fre-
quency converter to give a warning signal via one of the digital outputs.
Select
ETR Trip 1-4
if you want a trip when the motor is overloaded ac-
cording to the calculations.
NB!
This function cannot protect the individual motors in
the case of motors linked in parallel.
130
Start frequency
Value:
0.0 - 10.0 Hz
0.0 Hz
Function:
The start frequency is active for the time set in parameter 120
Start de-
lay
, after a start command. The output frequency will 'jump' to the next
preset frequency. Certain motors, such as conical anchor motors, need
an extra voltage/start frequency (boost) at start to disengage the me-
chanical brake. To achieve this parameters 130
Start frequency
and 131
Initial voltage
are used.
Description of choice:
Set the required start frequency. It is a precondition that parameter 121
Start function
, is set to
Start frequency/voltage clockwise
[3] or
Start fre-
quency voltage in reference direction
[4] and that in parameter 120
Start
delay
a time is set and a reference signal is present.
NB!
If parameter 123 is set higher than parameter 130, the
start delay function (parameter 120 and 121) will be
skipped.
131
Initial voltage
Value:
0.0 - 200.0 V
0.0 V
Function:
Initial voltage
is active for the time set in parameter 120
Start delay
, after
a start command. This parameter can be used for example for lifting/
dropping applications (conical anchor motors).
Description of choice:
Set the required voltage necessary to cut out the mechanical brake. It is
assumed that parameter 121
Start function
, is set to
Start frequency/
voltage clockwise
[3] or
Start frequency/voltage in reference direction
3 Programming
VLT® Decentral FCD
46
MG.04.B8.02 - VLT is a registered Danfoss trademark
3
Summary of Contents for VLT Decentral FCD 300
Page 112: ......