ENGLISH
18
During pump operation, keep well away from the moving parts (shaft, fan, etc.) unless it is absolutely necessary,
and only then wearing suitable clothing as required by law, to avoid being caught.
6.3.2.
Noise level
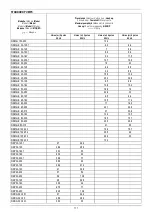
The noise levels of pumps with standard supply motors are indicated in table 6.6.2 on page 101. Remember that, in cases where
the LpA noise levels exceed 85 dB(A), suitable HEARING PROTECTION must be used in the place of installation, as required by
the regulations in force.
6.3.3.
Hot and cold parts
As well as being at high temperature and high pressure, the fluid in the system may also be in the form of
steam! DANGER OF BURNING ! ! ! It may be dangerous even to touch the pump or parts of the system.
If the hot or cold parts are a source of danger, they must be accurately protected to avoid contact with them.
6.3.4.
Any leaks of dangerous or harmful liquids (for example, from the shaft seal) must be conveyed and disposed of in accordance
with the regulations in force so as not to cause a risk or damage to persons and to the environment.
7.
INSTALLATION
The pumps may contain small quantities of residual water from testing. We advise flushing them briefly
with clean water before their final installation.
The electropump must be fitted in a well ventilated place, with an environment temperature not exceeding 40°C. As they have degree
of protection IP55, the electropumps may be installed in dusty and damp environments. If installed in the open, generally it is not
necessary to take any particular steps to protect them against unfavourable weather conditions. If the unit is installed in a location
where there is a risk of explosion, the local regulations on "Ex" protection must be respected, using only suitable motors.
7.1. Foundation
The buyer is fully responsible for preparing the foundation which must be made in conformity with the dimensions. Metal foundations
must be painted to avoid corrosion; they must be level and sufficiently rigid to withstand any stress. Their dimensions must be
calculated to avoid the occurrence of vibrations due to resonance.
With concrete foundations, care must be taken to ensure that the concrete has set firmly and is completely dry before placing the unit
on it. The surface that it sits on must be perfectly flat and horizontal. After the pump has been positioned on the foundation, check
with a spirit level to ensure that it is sitting perfectly level. If not, suitable shims must be inserted.
7.2. Connecting the pipes
Ensure that the metal pipes do not transmit excess force to the pump apertures, so as to avoid causing deformations or breakages. Any
expansion due to the heat of the pipes must be compensated with suitable precautions to avoid weighing down on the pump. The
counterflanges of the pipes must be parallel to the flanges of the pump.
To reduce noise to a minimum it is advisable to fit vibration-damping couplings on the intake and delivery pipes.
It is always good practice to place the pump as close as possible to the liquid to be pumped.
It is advisable to use a suction
pipe with a diameter larger than that of the intake aperture of the electropump. If the head at intake is negative, it is indispensable to
fit a foot valve with suitable characteristics at intake. Irregular passages between the diameters of the pipes and tight curves
considerably increase load losses. Any passage from a pipe with a small diameter to one with a larger diameter must be gradual.
Usually the length of the passage cone must be 5 to 7 times the difference in diameter.
Check accurately to ensure that the joins in the intake pipe do not allow air infiltrations. Ensure that the gaskets between flanges and
counterflanges are well centred so as not to create resistances to the flow in the pipes. To prevent the formation of air pockets, the
intake pipe must slope slightly upwards towards the pump.
If more than one pump is installed, each pump must have its own intake pipe. The only exception is the reserve pump (if envisaged)
which, as it starts up only in the case of breakdown of the main pump, ensures the operation of only one pump for each intake pipe.
Interception valves must be fitted upstream and downstream from the pump so as to avoid having to drain the system when carrying
out pump maintenance.
The pump must not be operated with the interception valves closed, as in these conditions there would be an increase in
the temperature of the liquid and the formation of vapour bubbles inside the pump, leading to mechanical damage. If there
is any possibility of the pump operating with the interception valves closed, provide a by-pass circuit or a drain leading to
a liquid recovery tank (following the requirements of local legislation concerning toxic fluids).
7.3. Calculating the NPSH
To guarantee good operation and maximum performance of the electropump, it is necessary to know the level of the N.P.S.H. (Net
Positive Suction Head) of the pump concerned, so as to determine the suction level Z1. The curves for the N.P.S.H. of the various
pumps may be found in the technical catalogue.
This calculation is important because it ensures that the pump can operate correctly without cavitation phenomena which occur when,
at the impeller intake, the absolute pressure falls to values that allow the formation of vapour bubbles in the fluid, so that the pump
works irregularly with a fall in head. The pump must not cavitate because, as well as producing considerable noise similar to metallic
hammering, it would cause irreparable damage to the impeller.
To determine the suction level Z1, the following formula must be applied:
Z1 = pb - rqd. N.P.S.H. - Hr - correct pV
where:
Z1
= difference in level in metres between the axis of the pump and the free surface of the liquid to be pumped
pb
= barometric pressure in mcw of the place of installation
(fig. 6 on page 108)
NPSH
= net load at intake of the place of work
(see characteristic curves in the catalogue)
Hr
= load loss in metres on the whole intake duct (pipe - curves - foot valves)
pV
= vapour tension in metres of the liquid in relation to the temperature expressed in °C
(see fig. 7 on page 108)