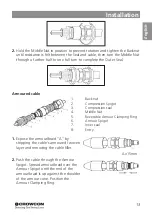
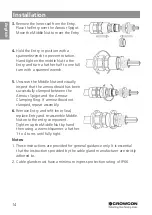
Installation
10
English
Follow the steps outlined below and the sample calculation shown in the next
section to calculate for specific applications.
1. The voltage must not fall below 10V, so start the calculation by setting the
voltage at the last detector in the line at that value.
2. Each detector may draw up to 0.070A. Calculate the cable voltage loss
of the first ‘hop’ between detectors by taking the current 0.070A and
multiply this by the cable resistance of the ‘hop’ between the last and the
last but one detector.
3. Add this voltage drop to the initial 10V to get the lowest acceptable
voltage at the last but one detector. Add 0.070A to the value for the
‘aggregate current’ to get to 0.14A, the minimum current running
through the last but one ‘hop’ of the bus. Multiply this by the cable
resistance for the last but one ‘hop’ to get the next voltage drop.
4. Repeat this process for each detector, accumulating the voltage losses that
will occur between each detector.
5. The maximum detector voltage of 30V must not be exceeded.
Example Calculation using the above rules
How many
Xsafe Bright
can be put on a multidrop cable if:
1. The controller has a guaranteed minimum output voltage of 18V.
2. Cable resistance is 12.1Ω/km.
3. There is 20m between each detector and 20m from the final detector to
the controller.
4. The worst case current draw (
Xsafe Bright
toxic) is 70mA.
Xgard Bright
Xgard Bright
Xgard Bright
Xgard Bright
Xgard Bright
Xgard Bright
1
2
3
4
5
6
Control
Panel