Wear
Radial shaft sealing rings are rubbing seals. Hence, they are subject to wear
and generate frictional heat.
Wear of the rubbing seal can be reduced only if lubrication is adequate and the
sealing point is clean. Here, the lubricant also acts as a coolant, supporting the
discharge of frictional heat from the sealing point.
●
Prevent the sealing point from becoming dry and dirty. Always ensure ad‐
equate cleanliness.
Under unfavorable ambient conditions (e.g. grinding dust, metal
shavings), maintenance could be necessary.
Resistance
The materials used for the radial shaft sealing rings are highly resistant to oils
and chemicals. The performance test for the particular operating conditions lies,
however, within the machine manufacturer’s responsibility.
Vertical installation positions
IM V3
The degree of protection on the flange side of motors with a shaft sealing ring
is IP 65. Hence, tightness is ensured only in case of splashing fluids. Fluid
levels present on the A-side require a higher degree of protection. If the motor
is installed in vertical position (shaft pointing up), the instructions in the section
”Design and Installation Positions” in this chapter must, in addition, be ob‐
served.
Note on construction
Rexroth recommends that any direct contact of the drive shaft and the radial
shaft sealing ring with the processing medium (coolant, material corrosion)
caused by the machine or system construction should be avoided.
9.10
Bearings and Shaft Load
9.10.1
General
During operation, both radial and axial forces act upon the motor shaft and the
motor bearings. The construction of the machine, the selected motor type and
the attachment of driving elements on the shaft side must be adapted to one
another to ensure that the load limits specified are not exceeded.
9.10.2
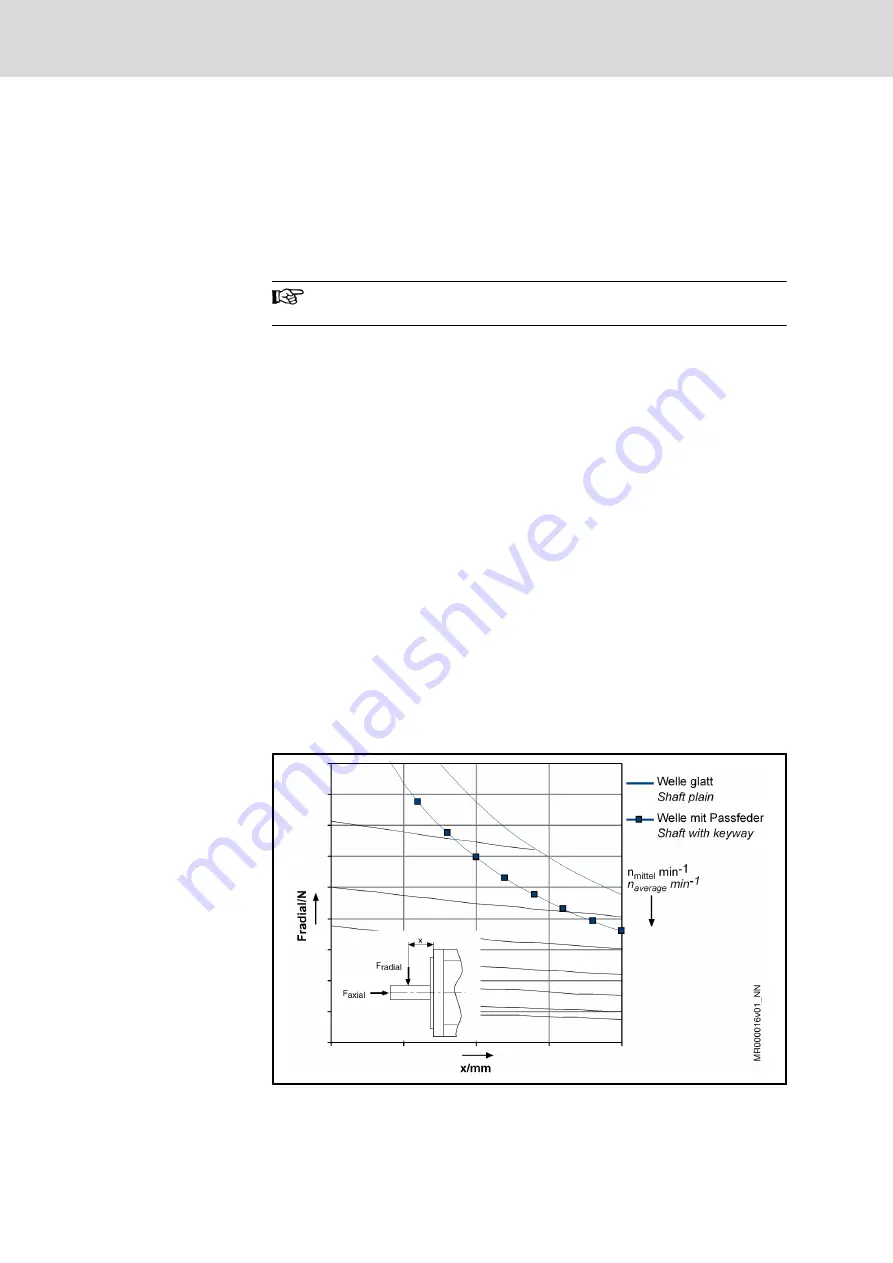
Radial Load, Axial Load
Fig.9-17:
Example of a shaft load diagram
86/131
Bosch Rexroth AG | Electric Drives
and Controls
Rexroth MKE Synchronous Motors | Project Planning Manual
Operating Conditions and Application Notes
















































