Parameterization and commissioning
EL6751
66
Version: 3.5
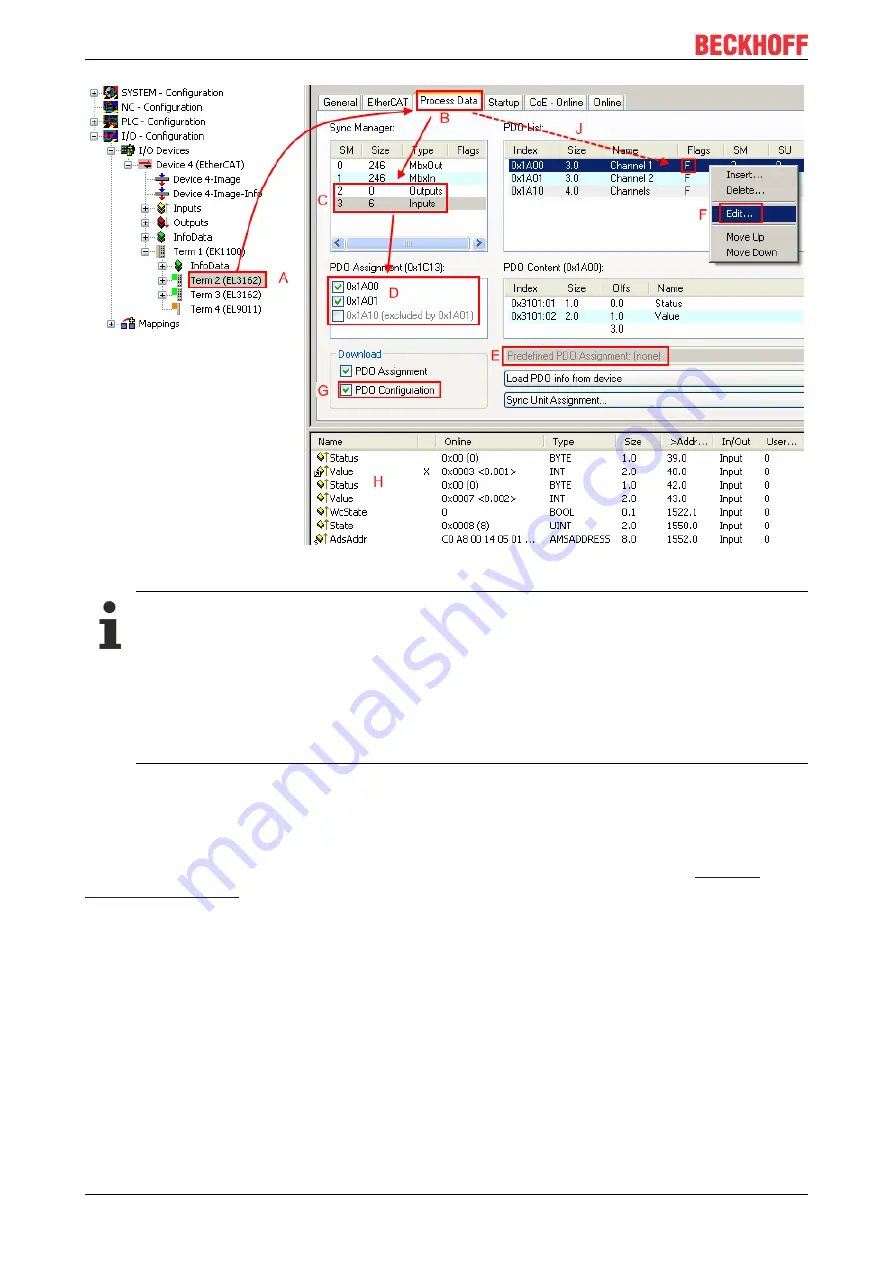
Fig. 79:
Configuring the process data
Manual modification of the process data
According to the ESI description, a PDO can be identified as “fixed” with the flag “F” in the PDO
overview (Fig.
“Configuring the process data”
, J). The configuration of such PDOs cannot be
changed, even if TwinCAT offers the associated dialog (“Edit”). In particular, CoE content cannot be
displayed as cyclic process data.This generally also applies in cases where a device supports
download of the PDO configuration, “G”.In case of incorrect configuration the EtherCAT slave usu-
ally refuses to start and change to OP state. The System Manager displays an “invalid SM cfg” log-
ger message:This error message (“invalid SM IN cfg” or “invalid SM OUT cfg”) also indicates the
reason for the failed start.
5.2
General Notes - EtherCAT Slave Application
This summary briefly deals with a number of aspects of EtherCAT Slave operation under TwinCAT. More
detailed information on this may be found in the corresponding sections of, for instance, the
.
Diagnosis in real time: WorkingCounter, EtherCAT State and Status
Generally speaking an EtherCAT Slave provides a variety of diagnostic information that can be used by the
controlling task.
This diagnostic information relates to differing levels of communication. It therefore has a variety of sources,
and is also updated at various times.
Any application that relies on I/O data from a fieldbus being correct and up to date must make diagnostic
access to the corresponding underlying layers. EtherCAT and the TwinCAT System Manager offer
comprehensive diagnostic elements of this kind. Those diagnostic elements that are helpful to the controlling
task for diagnosis that is accurate for the current cycle when in operation (not during commissioning) are
discussed below.
















































